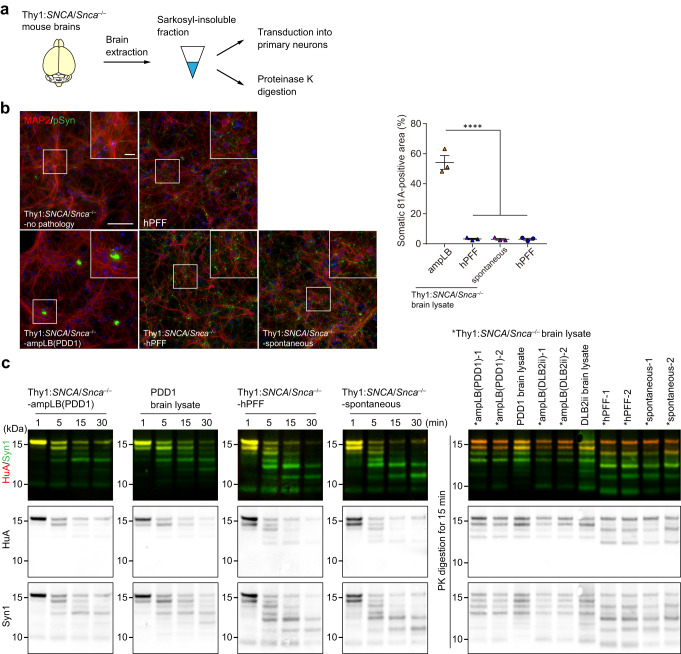
Fig. 7. AmpLB-induced pathological αSyn in Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/– mice maintains the biological and conformational features of original LB-αSyn.
a Schematic representation of experimental design. b Left panels: Mouse primary hippocampal neurons treated with brain lysates of Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/– mice without αSyn pathology (Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/–-no pathology), ampLB-injected Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/– mice (Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/–-ampLB), hPFF-injected Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/– mice (Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/–-hPFF), and old Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/– mice with spontaneous αSyn pathology (Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/–-spontaneous), and hPFF. Immunocytochemistry with MAP2 and pSyn (81 A) antibodies. Scale bars 100 µm, 20 µm (inset). Right panel: Percent of total pSyn-positive pathology in somatic inclusions (n = 3 independent wells per group). One-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s post hoc test was performed (Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/–-ampLB vs. Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/–-hPFF, Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/–-spontaneous, hPFF p < 0.0001). Scale bar 10 µm. c Proteinase K (PK) digestion on Thy1:SNCA/Snca–/– mouse brain lysate and LBD brain lysate. Left panels: Samples were subjected to PK digestion for 1, 5, 15, and 30 min, followed by western blot analysis with anti-human αSyn antibodies HuA and Syn1. Right panel: Samples were subjected to PK digestion for 15 min, followed by western blot analysis with HuA and Syn1 antibodies. Images are representative of two independent experiments. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.