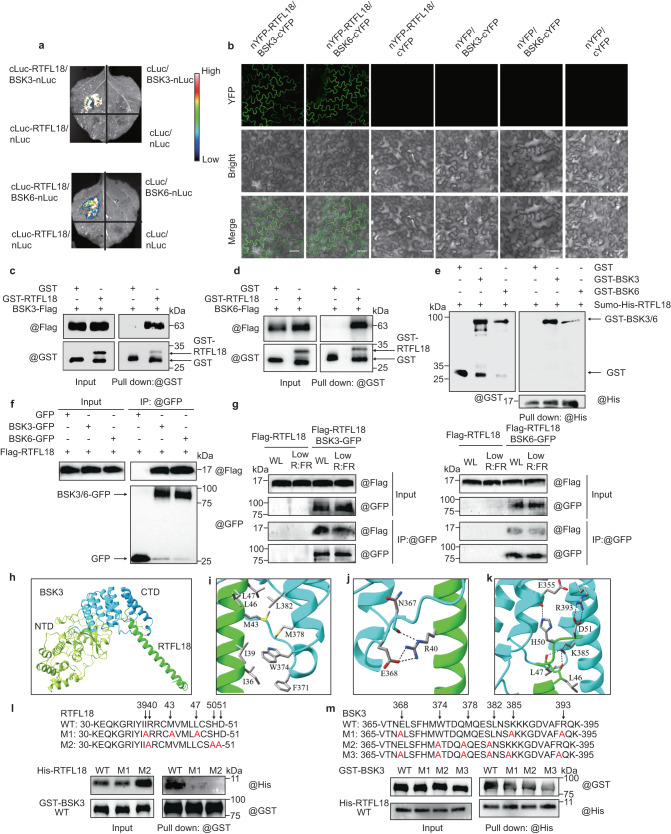
Fig. 4. RTFL18 interacts with BSK3 and BSK6.
a Interactions between RTFL18 and BSK3/BSK6 were detected by luciferase complementary imaging (LCI). b Interactions between RTFL18 and BSK3/BSK6 were detected via bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays. YFP, YFP signal; Bright, bright field; Merge, merged image of YFP signal with bright field. Scale bars represent 50 μm. c, d Interactions between RTFL18 and BSK3/BSK6 were detected via semi-in vivo pull-down assay. e Interaction between RTFL18 and BSK3/BSK6 were detected via in vitro pull-down assay. f Interactions between Flag-RTFL18 and BSK3/6-GFP were detected via coimmunoprecipitation (CoIP) assay in N. benthamiana leaf cells. g Interactions between Flag-RTFL18 and BSK3/BSK6-GFP were detected via coimmunoprecipitation (CoIP) assay in Arabidopsis. h The BSK3/RTFL18 complex was predicted with AlphaFold-Multimer. The N-terminal domain (NTD) and C-terminal domain (CTD) of BSK3 are green yellow and cyan, respectively. RTFL18 is green. i The hydrophobic interactions between BSK3 and RTFL18. j Hydrogen bond interactions between BSK3 and RTFL18. k The hydrogen bond and electrostatic interactions between BSK3 and RTFL18. l Interactions between different forms of RTFL18 and BSK3 were detected via in vitro pull-down assays. 6His-RTFL18 WT (wild type), M1 (I39A, M43A, L47A), M2 (I40A, H50A, D51A), and GST-BSK3 were expressed in and purified from E. coli. Anti-GST antibodies were used to pull down GST-BSK3. Both the immunoprecipitated fractions and inputs were analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-His and anti-GST antibodies, respectively. m Interactions between different forms of BSK3 and RTFL18 were detected via in vitro pull-down assays. GST-BSK3 WT (wild type), M1 (E368A, K385A, R393A), M2 (W374A, M378A, L382A), M3 (E368A, K385A, R393A, T374A, M378A, L382A) and His-RTFL18 were expressed in and purified from E. coli. Anti-His antibodies were used to pull down His-RTFL18. In b–g and l, m, each experiment was repeated three times with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.