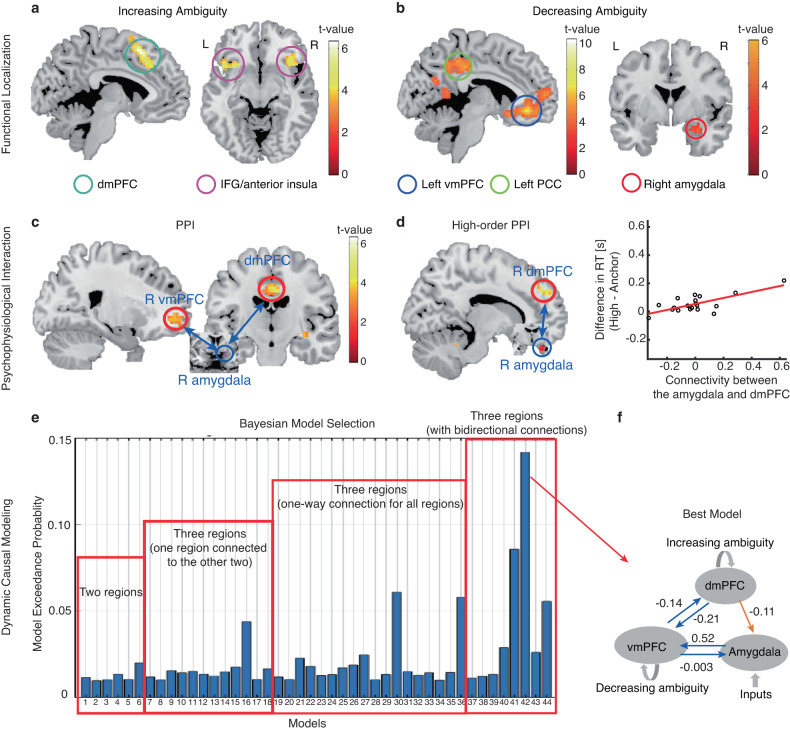
Fig. 2. Psychophysiological interaction (PPI) and dynamic causal modeling (DCM).
a, b Functional localization. a Increasing ambiguity was correlated with increasing BOLD activity in the bilateral dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC) and inferior frontal gyrus (IFG)/anterior insula. The generated statistical parametric map was superimposed on anatomical sections of the standardized MNI T1-weighted brain template. L left, R right. b Decreasing ambiguity was correlated with increasing BOLD activity in the right amygdala, left ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), and posterior cingulate cortex (PCC). c PPI analysis revealed functional connectivity between the amygdala and vmPFC as well as between the amygdala and dmPFC. d High-order PPI revealed functional connectivity between the amygdala and dmPFC. In the right plot, each dot represents a participant (n = 19), and the red line represents the linear fit. e Exceedance probability for each individual DCM model. Individual models are grouped into families (shown in red rectangles). f The best model shows a bidirectional connection between the vmPFC and amygdala, a bidirectional connection between the dmPFC and vmPFC, and a unidirectional connection from the dmPFC to the amygdala. Numbers show the mean of the maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimates of the optimal model.