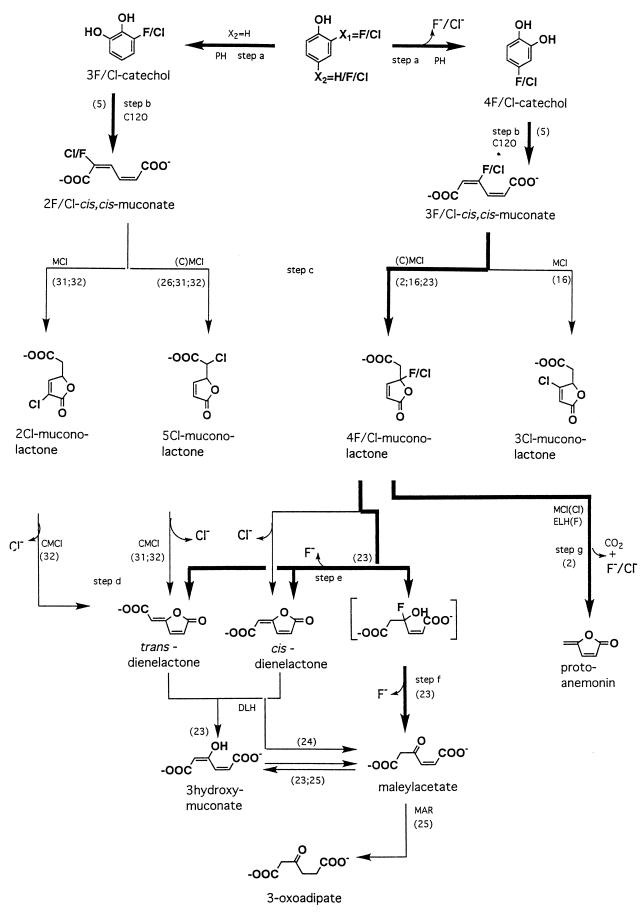
FIG. 3.
Pathways for the biodegradation and oxidative biodehalogenation of phenol and its halogenated analogs. Numbers in parentheses refer to literature references. The enzymes involved are indicated as follows: PH, phenol hydroxylase; C12O, catechol 1,2-dioxygenase; (C)MCl, (chloro)muconate cycloisomerase; DLH, dienelactone hydrolase; ELH, enol-lactone hydrolase; MAR, maleylacetate reductase. Pathways identified so far for fluorophenols, either in the literature or in the present study for E. jeanselmei, are indicated in boldface.