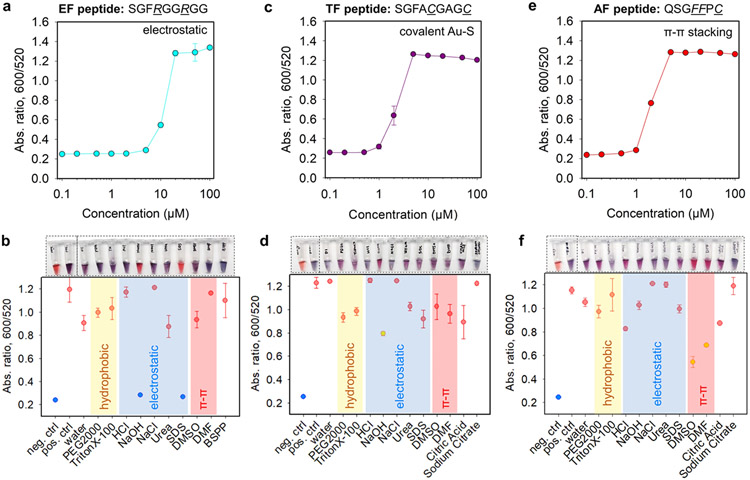
Figure 4.
Aggregation titration of the representative paired (a) EF/BSPP-AuNPs, (c) TF/citrate-AuNPs, and (e) AF/citrate-AuNPs where the critical coagulation concentrations were determined to be about 10, 2, and 2 μM, respectively. EF = electrostatic fragment; TF = thiolate fragment; and AF = aromatic fragment. (b, d, f) White-light image (top) and quantified reversal color change (bottom) of the peptide/AuNP aggregates in different surfactant solutions (10 mM, 100 μL) or solvents (100 μL). Negative control used the AuNPs only, and positive control used the peptide/ AuNP aggregates only. The yellow area indicates dominant hydrophobic interactions, the blue area indicates prevalent electrostatic interactions, and the red area implies strong π–π stacking forces. Error bars = standard deviations (n = 3).