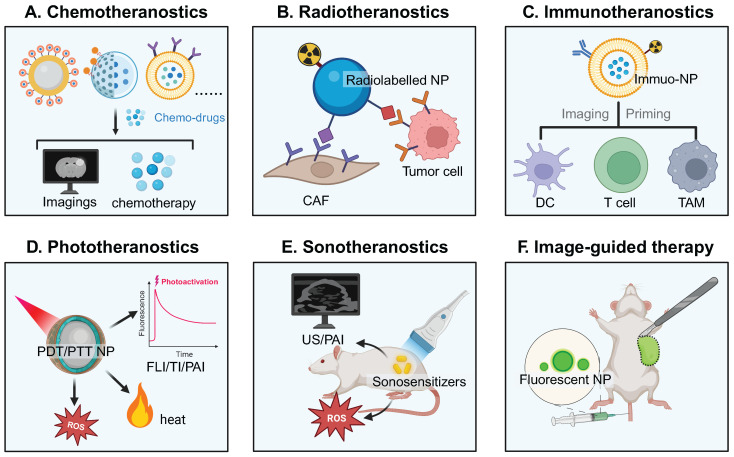
Figure 2.
Schematic of nanomedicine in different theranostic regimes based on treatment approaches. A) Chemotheranostics: various nanoformulations deliver chemotherapeutic molecules (some of them are optically visible) and imaging agents. B) Radiotheranostics: diagnostic/therapeutic radionuclides-labeled nanoparticles target tumor cells or CAFs. C) Immunotheranostics: nanomedicine is designed to image and prime immune cells, including DCs, T cells, and TAMs. D) Phototheranostics: light induces response from nanomedicine to generate imaging signals in FLI/TI/PAI or exert therapeutic effects of therapeutic agents (ROS and heat) in fluorescence imaging-guided PDT and/or PAI-guided PTT. E) Sonotheranositcs: ultrasound at a low intensity triggers sonosensitizers to improve ultrasound imaging contrast and/or generate toxic ROS in tumor cells. F) Image-guided therapy including image-guided surgery and image-guided cell therapies: pre-injection of fluorescent NPs or other optically visible probes aids in delineating tumor margins or sentinel lymph nodes for surgery. NP: nanoparticle; CAF: cancer-associated fibroblast; DC: dendritic cell; TAM: tumor-associated macrophage; FLI: fluorescence imaging; TI: thermal imaging; ROS: reactive oxygen species; US: ultrasound; PAI: photoacoustic imaging.