Table 1.
Selected activatable ligands toward endogenous/exogenous stimuli
| Stimulus | Activatable ligand and descriptions | Chemical structure or transition process | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Amide bond or bridge: cleavage |
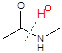
|
68 |
| Acetal bond: cleavage |
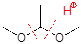
|
69 | |
| Poly(β-amino esters): amine protonation |
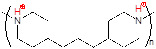
|
70 | |
| GSH | Disulfide bond: cleavage |
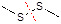
|
71 |
| Diselenide bond: cleavage |
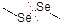
|
72 | |
| ROS | 1O2-activatable thioketals: cleavage |
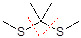
|
73 |
| H2O2-activatable ferrocene: hydrophobic to hydrophilic transformation |
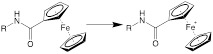
|
74 | |
| H2O2-sensitive phenylboronic acid |
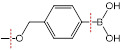
|
75 | |
| Enzyme | MMP2-cleavable peptide PLGIAG |
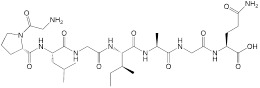
|
76 |
| Caspase 3/7-cleavage DEVD peptide (Asp-Glu-Val-Asp) |
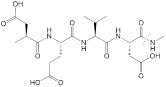
|
27 | |
| Cathepsin B-cleavage GFLG tetrapeptide (Gly-Phe-Leu-Gly) |
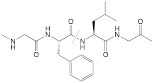
|
77 | |
| GGT-cleavage γ-glutamyl moieties |
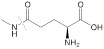
|
78 | |
| Hypoxia | A cleavable p-nitrobenzyl group by nitroreductase |
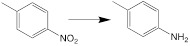
|
79 |
| Azobenzenes (AZO): reduction |
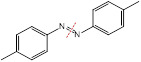
|
80 | |
| 2-nitroimidazole: hydrophobic to hydrophilic transformation |
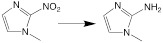
|
81 | |
| Light | Photocleavable linker (PCL) |
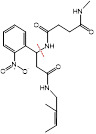
|
82 |
| Photolysis of O-nitrobenzyl ester |
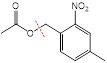
|
83 | |
| Light-cleavable coumarin ester |
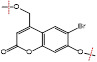
|
84 | |
| US | pMEMA: poly(methoxyethyl methacrylate) |
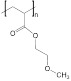
|
85 |
| Indirect breakage of thioketal bonds with the aid of a sonosensitizer |
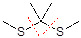
|
86 | |
| Cleavage of ACVA C-N bonds |
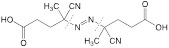
|
87 | |
| Ionizing radiation | Reduction of N-oxide |

|
88 |
| Diselenid bond: cleavage |
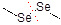
|
89 | |
| Geometrical structure transformation: cis-GdAzo to trans-GdAzo |
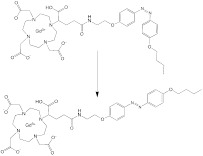
|
90 | |
| Thermal | Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) |
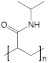
|
91 |
| Poly[(N-N-diethyl)acrylamide] (pDEA) |
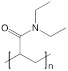
|
92 | |
| Dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine (DPPC): gel to liquid-crystalline phase transition |
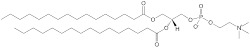
|
93 |
MMP2: matrix metalloproteinase 2; GGT: gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; US: ultrasound; ACVA: 4,4'-Azobis(4-cyanovaleric acid).
