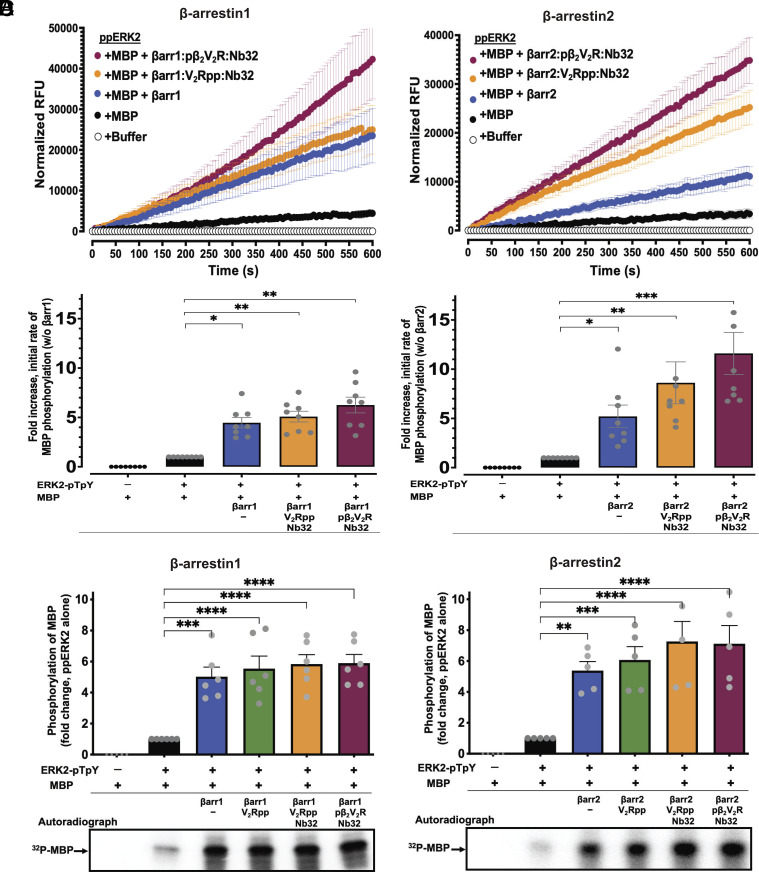
Fig. 6.
β-arrestins enhance the activity of dually phosphorylated ERK2-pTpY to phosphorylate MBP. (A and B, Top panels) Time courses of ERK2-pTpY-catalyzed phosphorylation of MBP as assessed using real-time fluorescence-based kinase assay in the absence or presence of basal state βarr1 (A) or βarr2 (B) or each in their active state forms (bound to V2Rpp or pβ2V2R together with Nb32). Relative fluorescence unit (RFU) intensities were background corrected to account for any contribution from control reactions: ERK2-pTpY alone and ERK2-pTpY with βarr1/2. Corrected RFU values are plotted as a function of time. Initial rates were determined from curve fitting of the linear phase of the reactions using linear regression. (A and B, Lower panels) quantification of phosphorylation of MBP presented as fold-enhancement of initial rates from each profile (as shown in the Top panel) relative to vehicle control (absence of βarr treated as onefold). Error bars indicate ± SEM of the mean from at least seven independent experiments. (C and D) Endpoint format kinase activity of ERK2-pTpY- against MBP was performed using [γ-32P] ATP as phosphate source in the absence or presence of βarr1 (C) or βarr2 (D) or their active state forms. Samples were separated on SDS-PAGE and 32P incorporation was assessed by autoradiography using a PhosphorImager. (C and D, Top panels) represent bar graphs of quantifications of phosphorylation levels of MBP under the indicated conditions. Lower panels in C and D show representative autoradiograms. Data are means ± SEM of at least five independent experiments. Asterisks indicated the significant difference based on one-way ANOVA analysis with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, and ****P ≤ 0.0001).