Extended Data Fig. 5 |. Assessment of ppsC homopolymeric tract mutations.
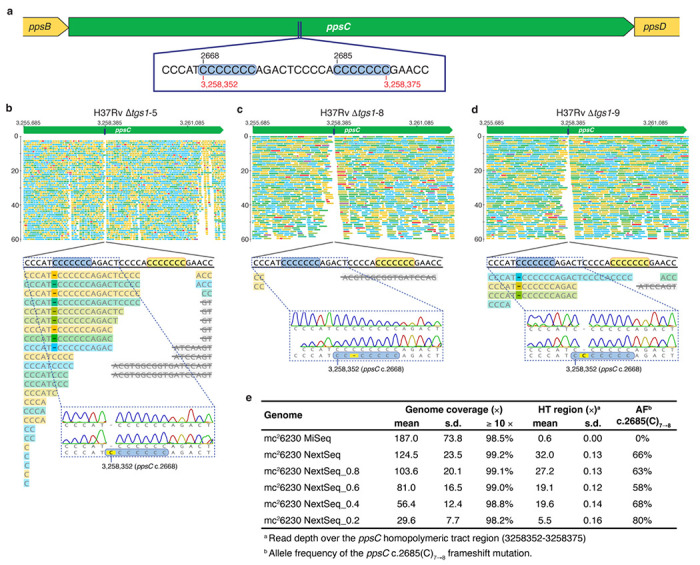
a, Schematic showing the location of a homopolymeric tract region in the ppsC gene. Sequence inserts show two adjacent 7-cytosine homopolymeric tracts (c.2668 and c.2685) ± 5 bp on either side. Numbers in black indicate the position in the ppsC gene and numbers in red the genomic position in the H37Rv genome. b–d, Analysis of the ppsC homopolymeric tract region in Δtgs1 mutants and identification of frameshift variants. WGS variant calling failed to identify PDIM mutations in Δtgs1-5, Δtgs1-8 and Δtgs1-9 despite a PDIM(−) result in VAN-P MICs (Fig. 2b) and validation of Δtgs1-9 as PDIM(−) by TLC (Fig. 2c). Close manual inspection of WGS reads showed the ppsC homopolymeric tract region is poorly covered by Illumina MiSeq and identified potentially missed variant calls. PCR and Sanger sequencing confirmed the presence of a 2668(C)7→6 frameshift mutation in both Δtgs1-5 (b) and Δtgs1-9 (d) and identified a 2668(C)7→8 mutation in Δtgs1-8 that was not covered at all by WGS (c). (b–d) were created with Geneious Prime® 2022.2.2 and Illustrator 26.4.1. Coverage has been cropped to a read depth of 60 ×. e, Identification of an unfixed ppsC c.2685(C)7→8 frameshift mutation in mc26230 by Illumina NextSeq. VAN-P assays and TLC lipid analysis determined mc26230 is highly PDIM deficient (Fig. 1a,c,e), however, WGS initially failed to identify any PDIM mutations in this strain and we subsequently established our mc26230 stock is a mixed population (Extended Data Fig. 4h). Resequencing using the Illumina NextSeq platform identified an unfixed frameshift mutation in ppsC (c.2685(C)7→8) that was not detected by Illumina MiSeq due to poor coverage. To assess the relationship between overall coverage and coverage over the homopolymeric region NextSeq reads were randomly downsampled. The number following ‘NextSeq_’ represents the fraction of reads sampled (i.e. 0.8 = 80% of reads retained).
