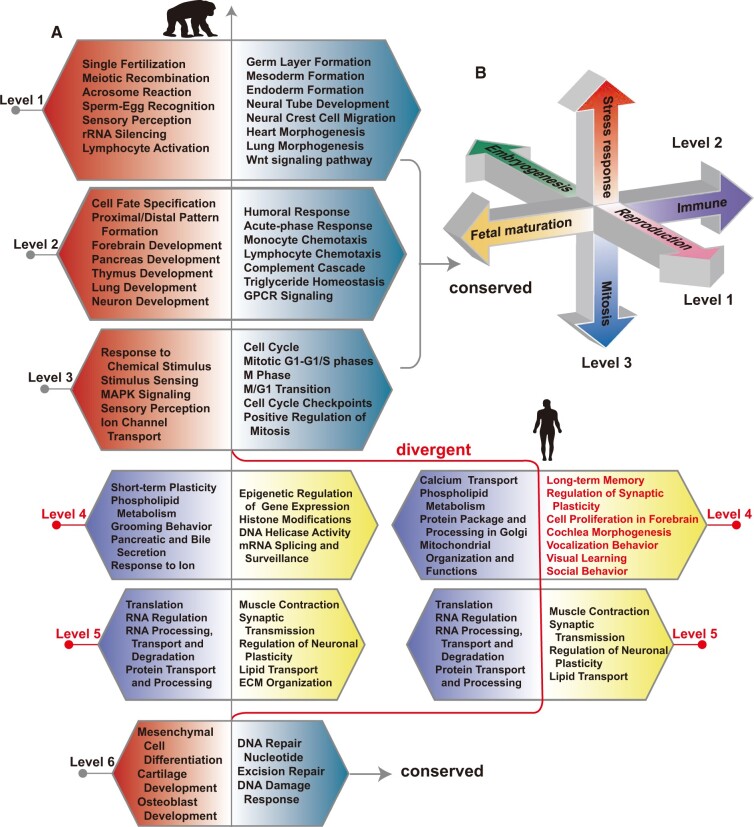
Fig. 3.
(A) Summarization of the biological processes enriched at the two ends of the top six polarized gene eigenvectors for humans and chimpanzees. Each box, whose poles are marked in two different colors, corresponds to one polarized gene eigenvector. From top to bottom, the six polarized gene eigenvectors are arranged in the descending order of their singular values. The enrichment results of the top three and the sixth gene eigenvectors are highly conserved in consistency with the results of the motif eigenvectors, therefore, only the results for human are shown. Significant divergences in the fourth and fifth eigenvectors are observed between humans and chimpanzees. Notably, the GO categories of regulation of synaptic plasticity, social behavior, vocalization behavior, visual learning, and long-term memory are enriched at the human fourth gene eigenvector, but are not so at that of chimpanzee. (B) The key functions of the top three CREF eigen-modules are represented by three polarized axes. They are highly conserved in humans, chimpanzees, and orangutans. Reproduction and embryogenesis lie at the two poles at the top level. Fetal maturation faces immune system at level 2. Stress responses and mitosis stay opposite in the level 3 axis. They are supported primarily by the enrichment results of the polarized gene eigenvectors, and are also supported by the known cis–trans regulation such as those in embryogenesis and mitosis due to the duality.