FIG. 1.
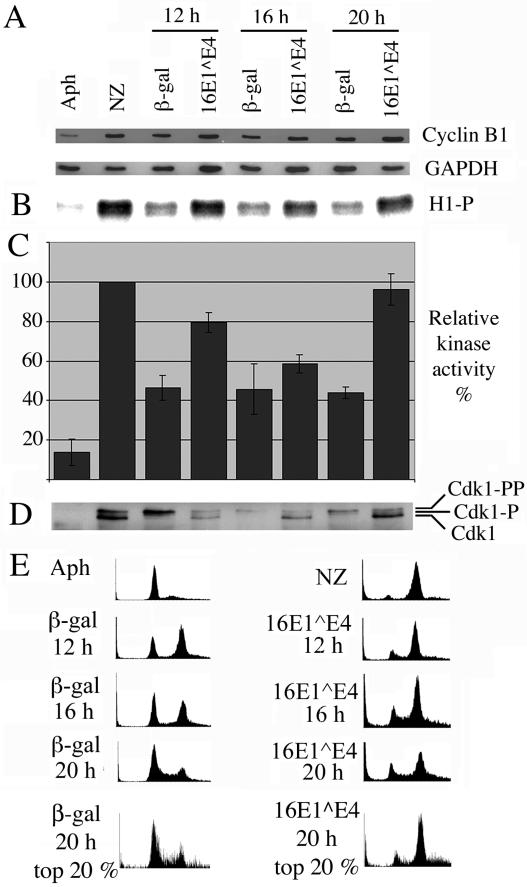
16E1∧E4 expression does not inhibit Cdk1/cyclin B kinase activity. Control G1/S-synchronized SiHa cells were either harvested without releasing the G1/S block (Aph) or released from the block for 6 h and then treated for 12 h with nocodazole prior to harvesting (NZ). G1/S-synchronized SiHa cells infected with recombinant adenoviruses expressing β-galactosidase or 16E1∧E4 were harvested at 12, 16, and 20 h post-block release. (A) Cell extracts were Western blotted for cyclin B1 and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). (B) Cdk1/cyclin B1 was immunoprecipitated from cell extracts and used in an in vitro kinase assay to phosphorylate histone H1. Protein labeled with 32P was detected with a phosphorimager. (C) Levels of histone H1 phosphorylation were quantitated with ImageQuant software and expressed as a percentage of that obtained for the nocodazole-treated samples. The results show the means of four experiments ± standard error of the mean. (D) Immunoprecipitated complexes were Western blotted for Cdk1. (E) Cells were stained with propidium iodide, immunostained for β-galactosidase or 16E1∧E4, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Plots show cell number versus DNA content. The final row shows plots in which the top 20% of high-β-galactosidase- or 16E1∧E4-expressing cells were selected for analysis of DNA content.