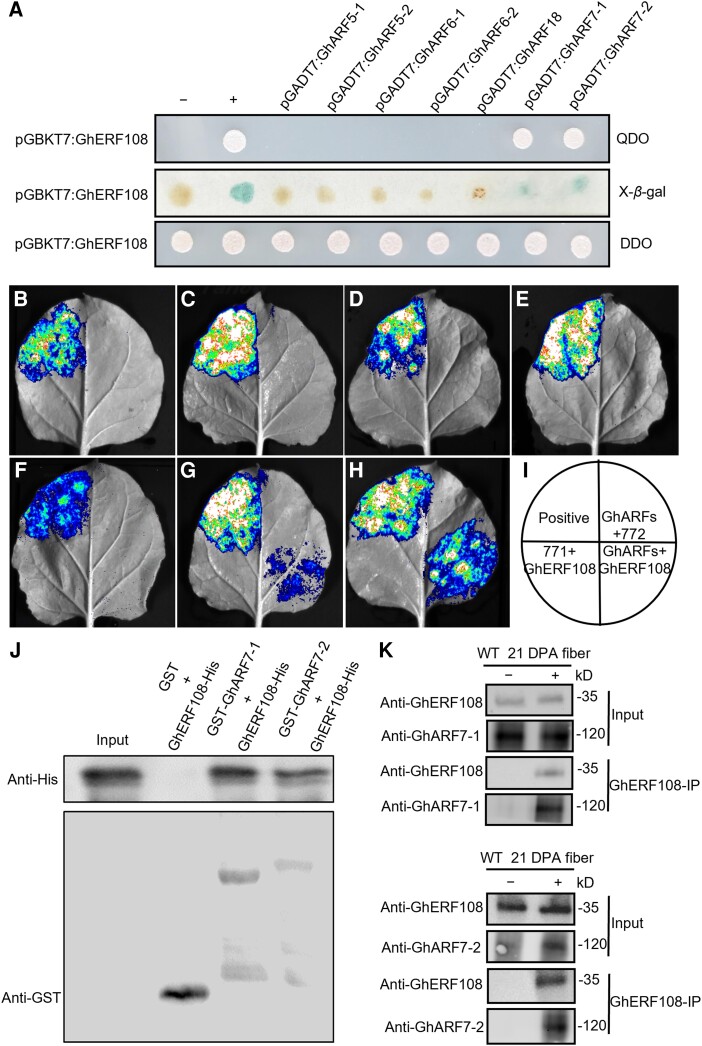
Figure 3.
GhERF108 interacts with GhARF7-1 and GhARF7-2. A) Y2H assay of GhERF108 protein interacting with GhARFs, using pGADT7 + pGBKT7-lam as a negative control and pGADT7-T + pGBKT7-53 a as positive control. (Middle) Flash-freezing filter assay of the β-galactosidase activity. (Upper and bottom) Yeast transformants streaked on QDO medium (SD/-Trp/-Leu/-His/-Ade) and DDO medium (SD/-Trp/-Leu), respectively. B to H) LCI assay of GhERF108 protein interacting with GhARF5-1 B), GhARF5-2 C), GhARF6-1 D), GhARF6-2 E), GhARF18 F), GhARF7-1 G), and GhARF7-2 H). LUC luminescence intensities represent their binding activities. I) Schematic diagram of B-H in LCI assay. J) Pull-down assay of GhERF108 protein interacting with GhARF7-1 and GhARF7-2 protein in vitro, respectively. GhERF108-His protein was incubated with GST-GhARF7-1 or GST-GhARF7-2 protein in vitro, using GST protein as a control. The precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-His or anti-GST antibody. K) Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay of GhERF108 with GhARF7-1 or GhARF7-2 in 21 DPA fibers of WT cotton. Soluble proteins were extracted in 21 DPA fibers of WT before (input) or after (IP) immunoprecipitation with anti-GhERF108 antibody and then detected by immunoblot with anti-GhERF108 (Cys-DGESPTQNGVAPQDS), anti-GhARF7-1 and anti-GhARF7-2 antibodies, respectively.