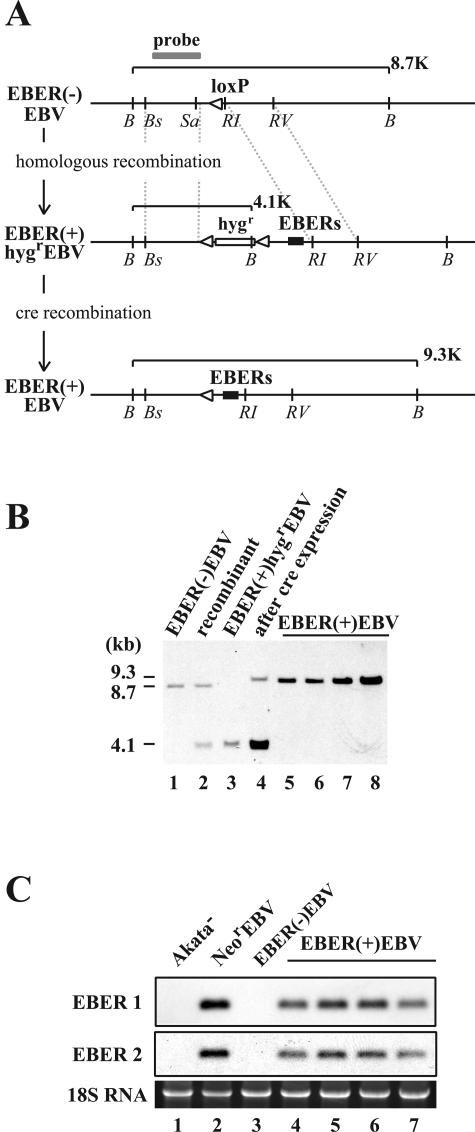
FIG. 4.
(A) Map of the genome of Akata strain EBV surrounding the EBER locus before and after the EBER knock-in. The EBER genes were reconstituted in the genome of EBER(−)EBV via homologous recombination by using the hygromycin resistance gene as a marker gene. Subsequently, the Hygr gene was removed by the transient expression of cre recombinase in Akata cells. The positions of restriction enzyme recognition sequences are indicated by B (BamHI), Bs (BstPI), Sa (SacI), RI (EcoRI), and RV (EcoRV). A gray line indicates a probe used for Southern blot analysis. White arrowheads indicate loxP sites. The EBER genes (black boxes) and the hygromycin resistance gene (hygr; open box) are also indicated. (B) Southern blot analysis of Akata cell clones harboring various recombinant EBVs.The results from an EBER(−)EBV-infected cell clone (lane 1), a targeted cell clone (recombinant; lane 2), an EBER(+)HygrEBV-infected cell clone (lane 3), the same cell clone with transient cre expression (lane 4), and EBER(+)EBV-infected cell clones (lanes 5 through 8) are shown. (C) Northern blot analysis of EBERs. The results from an EBV-negative Akata cell clone (Akata−; lane 1), a NeorEBV-infected cell clone (lane 2), a EBER(−)EBV-infected cell clone (lane 3), and EBER(+)EBV-infected cell clones (lanes 4 through 7) are shown.