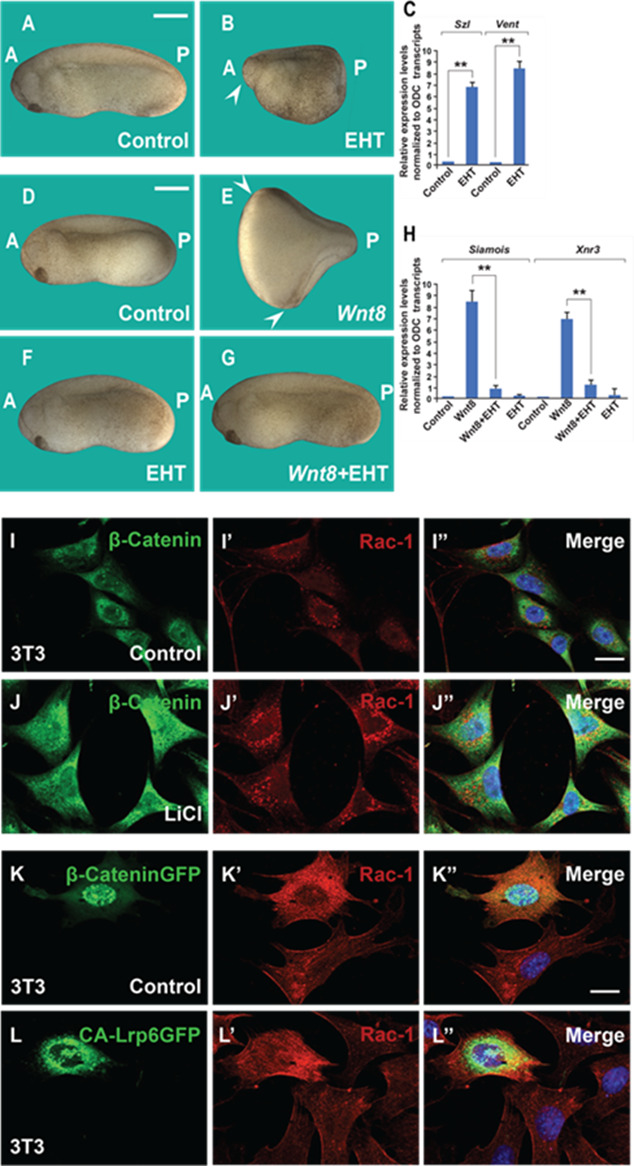
Figure 4. The Rac1 inhibitor EHT1864 blocks Wnt signaling in Xenopus embryos, and Rac1 levels are stabilized by treatments that increase Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
(A) Uninjected control embryo. (B) Incubation of the Xenopus embryos with the Rac1 inhibitor EHT at 32-cell stage (7 min, 10 mM) resulted in a ventralized phenotype with a small head in the anterior (A, arrowhead) and expanded ventral structures in the posterior (P). Rac1 activity is required for macropinocytosis, see Figure 4—figure supplement 1. (C) qRT-PCR of gastrula stage embryos showing increased ventral markers Szl and Vent1 after Rac1 inhibition. (D) Control embryo. (E) Injection of Wnt8. mRNA (2 pg) induces complete duplicated axes (arrows). (F) Injected embryos with EHT (1 mM, 4 nl 1x ventral) alone showed no phenotypic effect at this concentration. (G) EHT co-injected with Wnt8 mRNA blocked double axis formation. (H) qRT-PCR of Wnt target genes Siamois and Xnr3 at blastula confirming that Rac1 is required for early Wnt signaling. (I–J’’) Treatment of 3T3 cells with 40 mM Lithium Chloride (LiCl) increases β-catenin and Rac1 levels. (K–L’’) Transfection of 3T3 cells with stabilized constitutively active forms of β-cateninGFP or Lrp6GFP increased levels of Rac1 protein in transfected cells compared to untransfected ones. The numbers of embryos analyzed were as follows: A = 52, 100%; B = 47, 95% with ventralized small head phenotype; D = 58, 100%; E = 67; 97%; F = 64, 96%; G = 62, 97%, four independent experiments. Scale bars for embryos 500 μm; scale bars for immunofluorescence, 10 μm. qRT-PCR experiments represent biological replicates. Error bars denote standard error of the mean (SEM) (n ≥ 3) (**p < 0.01).