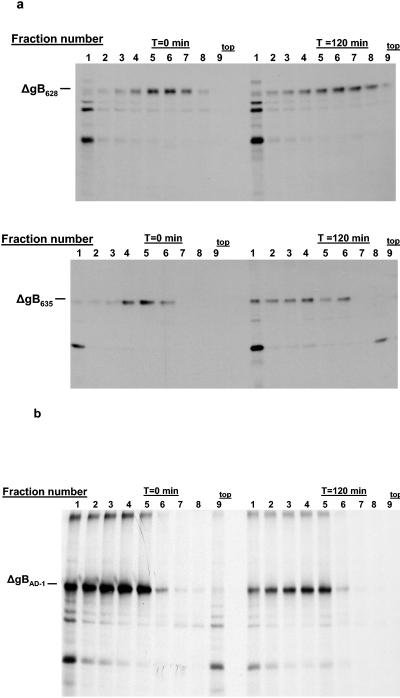
FIG. 4.
Oligomerization of gB mutants. (a) gB mutants ΔgB628 and ΔgB635 were expressed in monkey kidney cells by infection with recombinant vaccinia viruses and analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 3, except that the mutant protein was precipitated with MAb 758, which is directed at the NH2 terminus of gB. The mutant ΔgB628 protein failed to sediment further into the gradient at the later chase interval, indicating it did not form higher-molecular-weight multimers. In contrast, the ΔgB635 mutant protein formed higher-molecular-weight oligomers, as evidenced by its migration further into the gradient at the later chase interval. (b) gB mutant ΔgBAD-1 was expressed as a recombinant vaccinia virus and analyzed as described above. In this experiment, ΔgBAD-1 was precipitated with MAb 58-15, which is directed at the C terminus of gB. Note the similar distribution of the ΔgBAD-1 protein near the bottom of the gradient at both 0 and 120 min, indicating that this molecule likely aggregated shortly after its synthesis. The top of the gradient is indicated.