Figure 3. Autocrine RALFs function through FER/CVY1/ANJ/HERK1 receptors to form an inhibitory system at the stigma.
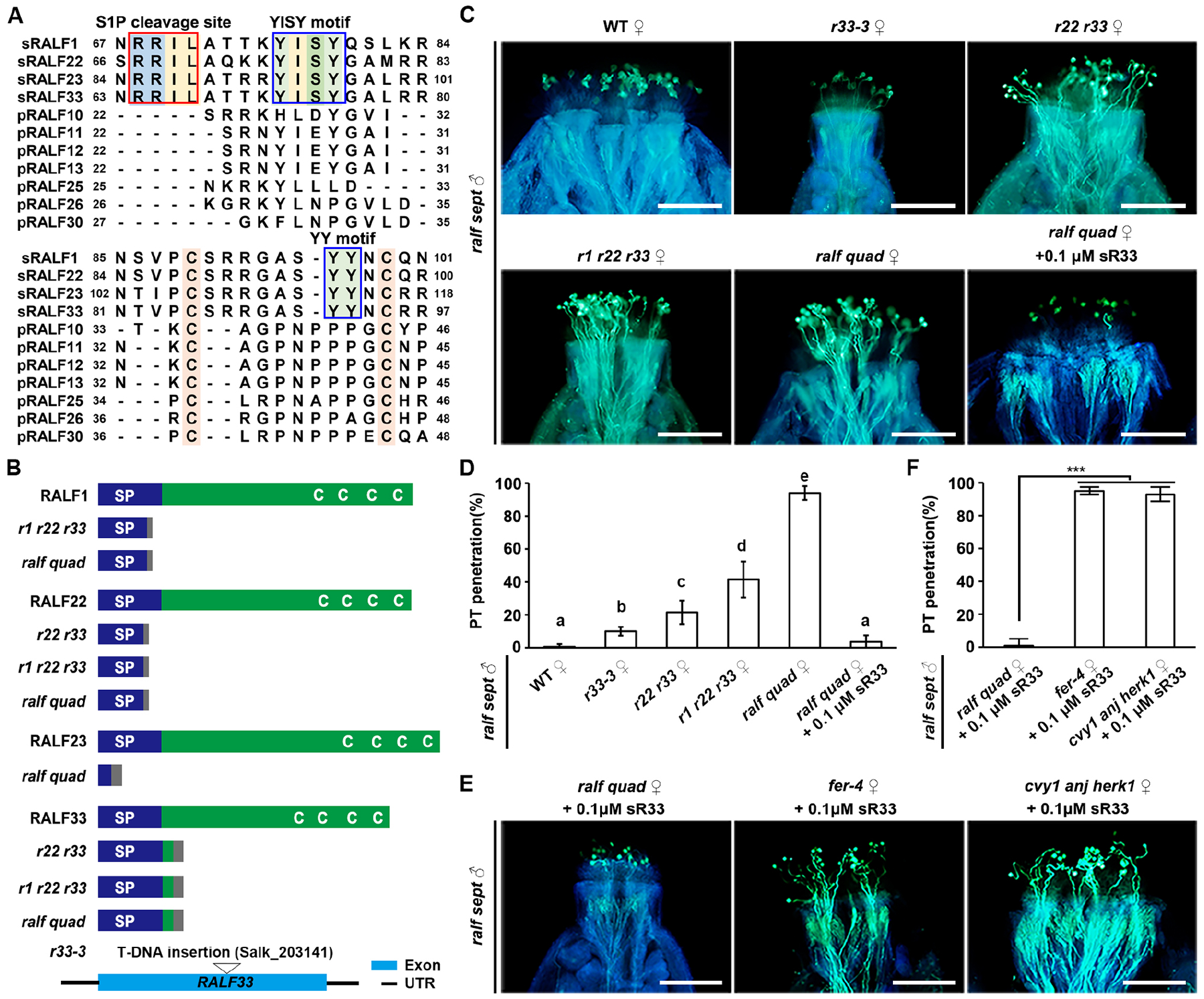
(A) Amino-acid alignment of pRALFs and sRALFs. Conserved residues are highlighted with colors. Boxes show conserved motifs as indicated.
(B) Schematic diagrams describing wild-type and CRISPR/Cas9-generated mutated peptide structures of sRALF1, 22, 23 and 33 in the double, triple and quadruple sRALF mutants. (Bottom) T-DNA insertional position in RALF33. C, conserved cysteine residues (Cs); SP, signal peptides. Gray boxes indicate missense sequences due to frame shift mutations.
(C) Aniline blue staining showing penetration status of ralf sept pollen tubes at 3 HAP in the stigmas of WT and sRALF mutants as indicated (ralf quad = r1 r21 r22 r33), as well as penetration of ralf quad stigmas pretreated with 0.1 μM synthetic sR33. Scale bars, 200 μm.
(D) Statistical analysis of pollen tube penetration shown in (C). Different letters represent significant differences between groups (P<0.001).
(E) Aniline blue staining showing penetration status of ralf sept pollen tubes at 3 HAP into the stigmas of ralf quad, fer-4 or cvy1 anj herk1, all of which were pretreated with 0.1 μM synthetic sR33. Scale bars, 200 μm.
(F) Statistical analysis of pollen tube penetration assayed in (F). Data in (D and F) are mean values ± SD; *** shows P<0.001 (Student’s t test). Each of the above assays was repeated at least three times.
See also Figure S4.
