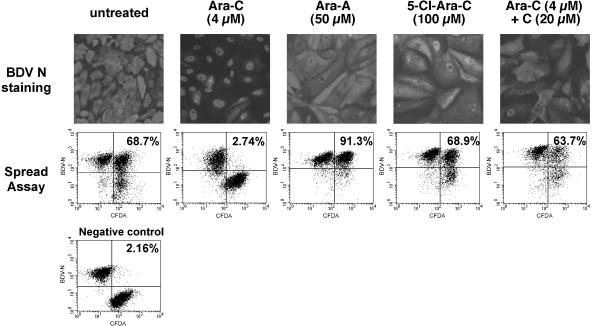
FIG. 1.
Representative examples of the inhibitory effects of compounds used in this study. (Top panels) Analysis by immunofluorescence of the subcellular localization of the BDV nucleocapsid protein (N) following treatment with different compounds. Vero-BV cells were treated for 5 days with the different compounds and stained with a rabbit anti-N polyclonal antibody, followed by a fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody. Of all compounds tested (only examples are shown here), only Ara-C resulted in nuclear retention of BDV N protein. Magnification, ×120 (original magnification, ×200). (Bottom panels) FACS analysis of BDV cell-to-cell spread. Confluent Vero cells were labeled with 5- (and 6-)carboxyfluorescein diacetate (CFDA) and were subsequently cocultivated for 5 days at a ratio of 1:1 with unlabeled Vero-BV cells. Cocultivation took place under daily treatment with 4 μM Ara-C or with various drugs (e.g., 50 μM Ara-A). Thereafter, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentage of viral dissemination during the cocultivation period was calculated as indicated in Table 1 and is shown in each case. Note that inhibition of BDV cell-to-cell spread is specific to Ara-C. The negative control consisted of a 1:1 mixture of CFDA-labeled Vero cells with Vero-BV cells, which were fixed directly after mixing.