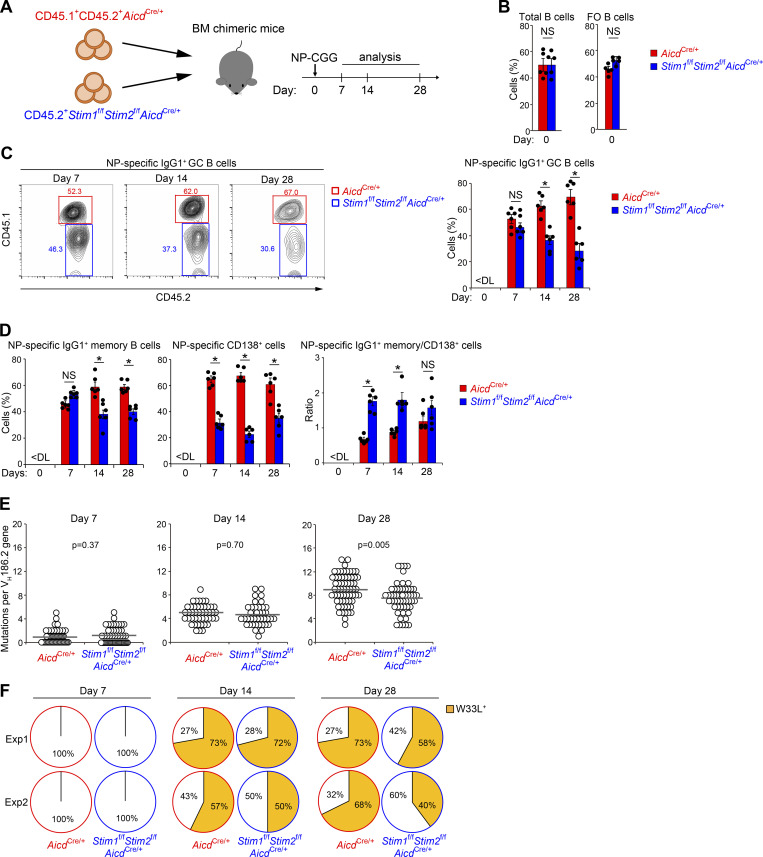
Figure 1.
STIM proteins are required for effective competition in GC. (A) Schematic of experimental workflow. Mixed BM chimeric mice (μMT mice lethally irradiated and reconstituted with 50% CD45.1+CD45.2+AicdCre/+ plus 50% CD45.2+Stim1f/fStim2f/fAicdCre/+ BM cells) were immunized with NP-CGG in alum. On the indicated time point (day 7∼28), the mice were sacrificed and analyzed. (B–D) Frequency of CD45.1+CD45.2+AicdCre/+ and CD45.2+Stim1f/fStim2f/fAicdCre/+ cells in indicated parental populations in the spleen of mixed BM chimeric mice before (B) and after immunization with NP-CGG in alum (C and D). Total B, follicular (FO) B, and NP-specific IgG1+ GC, IgG1+ memory B, and CD138+ cells are defined as B220+, CD21lowCD23highB220+, IgG1+NIP+CD38lowB220+, IgG1+NIP+CD38highB220+, and NIP+CD138+B220low cells, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for five or six mice. Data are representative of two independent experiments. NS, not significant. *, P < 0.05 versus AicdCre/+ cells ([B] Student’s t test and [C and D] two-way ANOVA). (E) Accumulation of mutations in VH186.2 genes of single NP-specific IgG1+ GC B cells in mixed BM chimeric mice immunized with NP-CGG in alum. Circles represent the number of mutations in individual clones. The results were evaluated statistically by Student’s t test. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (F) Frequency of W33L+ clones among NP-specific IgG1+ GC B cells in mixed BM chimeric mice immunized with NP-CGG in two separate experiments (Exp1 and Exp2). Numbers along the perimeter indicate percentages of W33L− (white) and W33L+ (orange) clones.