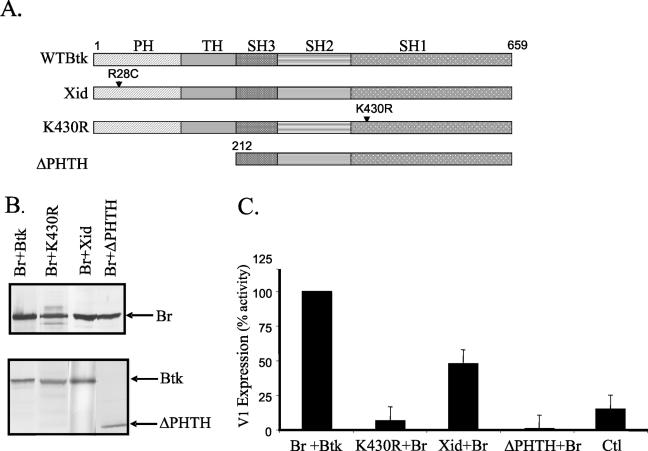
FIG. 4.
Functional Btk is required for Bright activity. (A) Schematic diagram depicting the pleckstrin (PH), tec (TH), and src (SH1 to -3) homology domains of wild-type Btk and the mutants used. R28C is the xid mutation; K430R renders Btk kinase inactive; ΔPHTH lacks the pleckstrin and tec homology domains. (B) Western blots showing expression of Bright (Br) and the Btk mutants in transfected CHO cell extracts. (C) V1 expression from the −574 full-length promoter construct was measured in CHO cells transfected with wild-type Bright and either wild-type or mutant Btk by real-time PCR as described in the previous figure legends. Each transfection was performed a minimum of three times, and data were calculated from triplicate samples in each experiment. Average values for each transfection are presented as percent activity of the values obtained with wild-type Btk plus Bright, which were set at 100%. Standard errors of the means are shown. Control transfected cells contained the empty Btk vector, the Bright reverse orientation vector, and the V1 reporter construct.