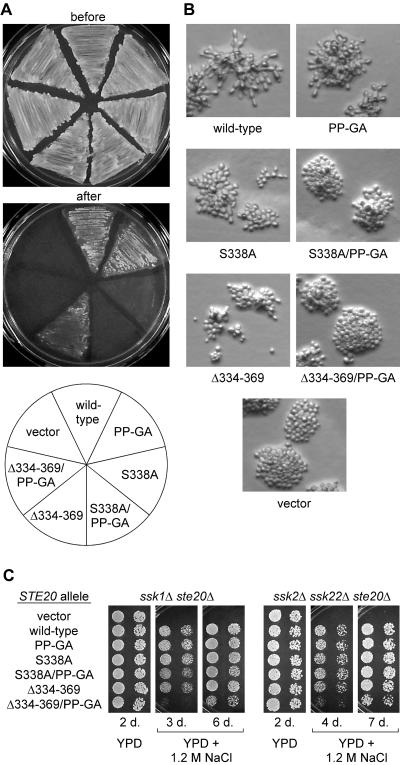
FIG. 6.
Effects of Ste20 PxxP mutations on filamentous growth and hyperosmotic resistance. (A) Agar invasion. Strain PPY1209 (Σ1278b ste20Δ) was transformed with the indicated GFP-Ste20 fusion constructs and assayed for invasive growth as described in Materials and Methods. Representative examples of cells remaining adherent after gentle rinsing with water, as well as before rinsing, are shown. Note that invasive growth conferred by the Δ334-369 allele is eliminated by the PP-GA mutation. (B) Filamentous colony morphology. The transformants used for panel A were grown on low-glucose medium for 24 h. Cells with wild-type Ste20 become elongated and form branched microcolonies under these conditions. Note that the disruption of these features becomes gradually more severe as mutations in the Cdc42-binding and Bem1-binding motifs are combined. (C) Hyperosmotic resistance. Strains PPY1287 (ssk1Δ ste20Δ) and PPY1646 (ssk2Δ ssk22Δ ste20Δ) were transformed with the indicated GFP-Ste20 fusion constructs. Fivefold serial dilutions were spotted onto YPD or YPD plus 1.2 M NaCl and incubated at 30°C for 2 to 7 days (d.) as indicated. Note that only the Δ334-369 PP-GA double mutant has a strong defect in osmoresistance and that even this mutant retains some function, as revealed at longer incubation times.