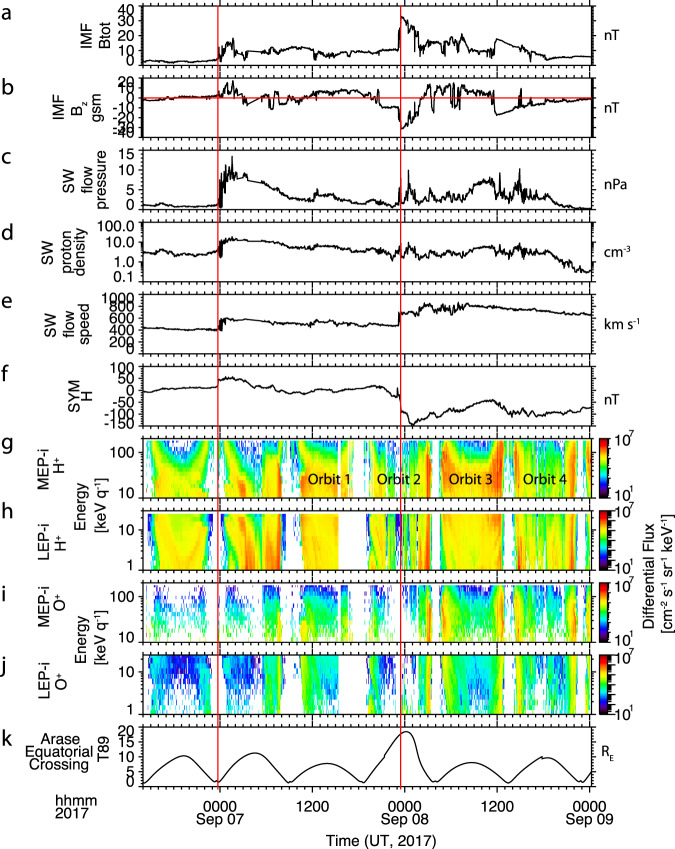
Fig. 3. Interplanetary driving conditions and Arase particle data for the full space weather event.
a, b Total and Bz component of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) from the OMNI dataset, propagated to the location of the Earth Bow Shock. c–e Solar Wind pressure, density and speed from the OMNI dataset propagated to the location of the Earth Bow Shock. f SYM-H index. g, h Differential energy flux for H+ from MEPi (10–180 keV) and LEPi (1–25 keV). i, j Differential energy flux for O+ from MEPi (10–180 keV/e) and LEPi (1–25 keV/e). k Equatorial crossing of the magnetic field line that passes through the Arase spacecraft, calculated using a T89 field model33. The red vertical lines indicate when the CMEs reach the nose of the bow shock. The red horizontal line in panel b indicates the zero line. The four orbits shown in Fig. 4 are labeled.