Fig. 7. Differential control of pluripotency factors and cellular decision-making through YAP levels and dynamics.
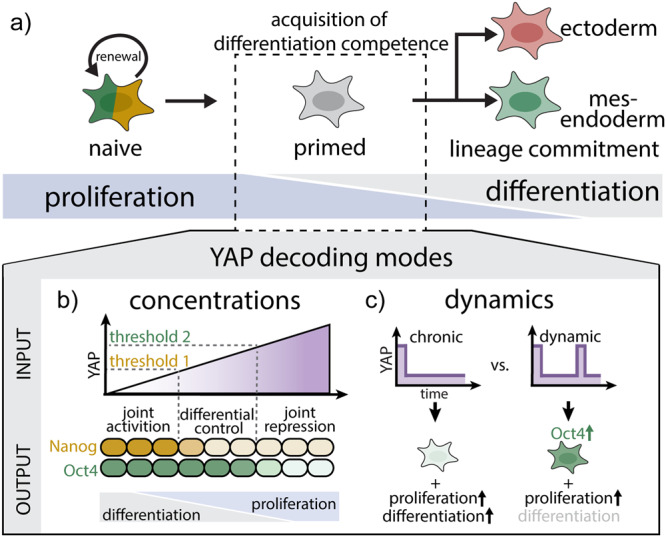
YAP concentrations and dynamics establish differential control strategies for pluripotency factors and developmental decision-making (proliferation, differentiation). a Top: Following pluripotency exit of naive mESCs, cells acquire signaling competence to interpret differentiation cues and transition to a primed state before committing to the ectodermal and mesendodermal lineages. The process is accompanied by progressive loss of proliferative potential. Bottom: Differential control strategies of cell behavior during the transition from pluripotency to lineage commitment through YAP levels and dynamics. b Decoding YAP steady-state concentrations through different sensitivity thresholds establish windows for the joint activation (low YAP) and repression (high YAP) or differential control (intermediate YAP) of Oct4 and Nanog. Across the YAP concentration range, steady-state levels have opposing effects on differentiation (YAP low) and proliferation (YAP high). c YAP dynamics enable the differential control of Oct4, cell differentiation, and proliferation. The different decoding modes depicted in b, c provide a means for the complex regulatory requirements of the pluripotency factors and cellular differentiation vs. proliferation.
