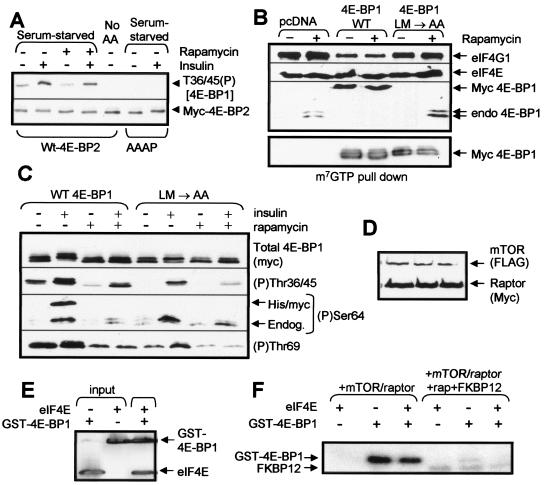
FIG. 6.
Features of 4E-BP2 and 4E-BP1 required for efficient phosphorylation in vivo. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with vectors for wild-type 4E-BP2 or a mutant in which the RAIP motif was altered to AAAP. Cells were starved of serum overnight and, in some cases, also of amino acids (60 min). Where indicated, cells were treated with rapamycin or insulin. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-myc (to detect 4E-BP2) or anti-4E-BP1 (Thr36/45 phosphospecific antibody). (B and C) HEK293 cells were transfected with vectors for WT 4E-BP1 or the LM/AA mutant, each as N-terminally his/myc-tagged proteins. After serum starvation overnight, cells were treated with rapamycin or insulin as indicated. (B) Samples of lysate were subjected to affinity chromatography on m7GTP-Sepharose prior to analysis of the bound material by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using the indicated antisera. (C) Samples of lysate were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-myc and the indicated phosphospecific antisera for 4E-BP1. For (P)Ser64, both the endogenous (endog.; serves as a positive control) and recombinant (his/myc) 4E-BP1 proteins can be seen. (D to F) HEK293 cells were transfected with vectors encoding FLAG-tagged mTOR and myc-raptor. (D) Western blot demonstrating that mTOR and myc-raptor are efficiently expressed. (E) GST-4E-BP1 and eIF4E were mixed and pulled down on glutathione-Sepharose (pull down), and the bound material was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using antisera for eIF4E and 4E-BP1. Purified eIF4E and GST-4E-BP1 (input) were run as controls. (F) Recombinant 4E-BP1 was incubated with immunoprecipitated mTOR/raptor in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP, MnCl2, and, where indicated, recombinant eIF4E and/or GST-FKBP12 plus rapamycin.