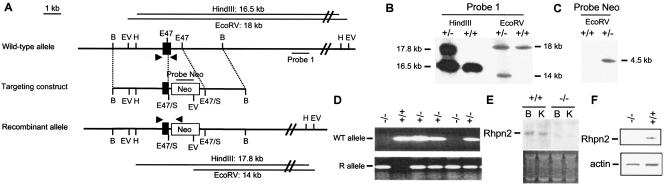
FIG. 2.
Targeted disruption of mouse Rhpn2. (A) Wild-type allele, targeting vector, predicted structure of the mutant allele, probes used in Southern blot analysis, DNA fragments generated after digestion with HindIII or EcoRV, and primers used for mouse genotyping by PCR (filled arrowheads). Filled boxes: exon 7 of the Rhpn2 gene. B, BamHI; EV, EcoRV; E47, Eco47III; E47/S, E47 DNA fragment ligated into SmaI-digested vector; H, HindIII. (B and C) Southern blots of the recombinant embryonic stem cell clone with probe 1 and the probe corresponding to the Neo cassette. Left and/or right margins, length of genomic DNA fragments generated after digestion with restriction enzymes (above blot). (D) Mouse genotyping by PCR amplification from tail DNA using primers specific for either the WT or the recombinant (R) allele. (E) RNA hybridization analysis of total brain (B) and kidney (K) RNA isolated from Rhpn2+/+ and Rhpn2−/− mice. The probe was a 2.2-kb dog rhophilin 2 cDNA fragment containing the complete coding region. (F) Western blot of brain protein extract from Rhpn2+/+ and Rhpn2−/− mice using anti-Rhpn2 or anti-actin antibody.