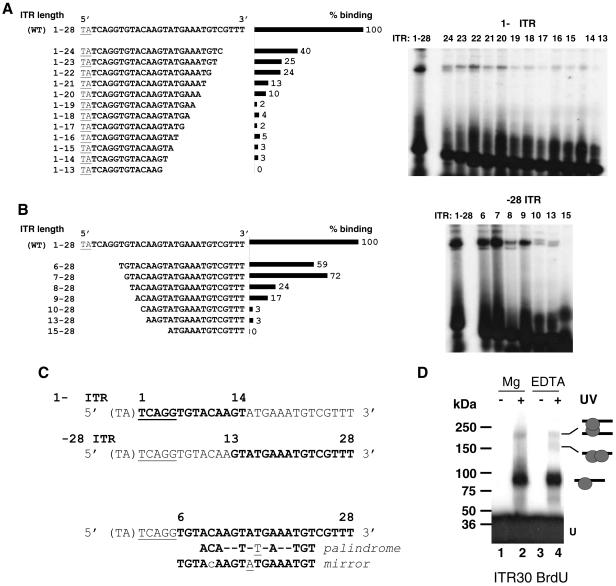
FIG. 6.
Mos1 ITR contains two binding sites for the Tnp. The wild-type ITR (WT) is the full-length sequence (TA + 28 bp). (A) EMSA with ITR truncated at the 3′ end (1-Δ). The sequences of the probes are given on the left. Binding rates obtained with the different 1-Δ ITR, expressed as percentages of that obtained for the WT ITR (taken as 100%), are shown in the center. EMSA data are presented on the right. (B) EMSA with ITR truncated at the 5′ end (Δ-28). The sequences of the probes are given on the left. Binding rates obtained with the different Δ-28 ITR, expressed as percentages of that obtained for the WT ITR (taken as 100%), are shown in the center. EMSA data are presented on the right. (C) Sequence data. The TA dinucleotide flanking the ITR is enclosed in parentheses. The cleavage signal (TCAGG) is underlined. Boldfaced letters represent the shortest sequence retaining a binding signal. The numbers above the top two sequences delineate the minimal truncated ITR that was able to interact with the Tnp. The symmetrical structures (palindrome or mirror) in truncated ITR, which fall between positions 6 and 28, are given at the bottom. The underlined nucleotide represents the center of each symmetrical structure. (D) UV cross-linking assays. SEC2 was assembled by using BrdU ITR30 as a probe with MgCl2 (lanes 1 and 2) or EDTA (lanes 3 and 4). Complexes were exposed to UV light (lanes 2 and 4) or not (lanes 1 and 3) and then loaded onto SDS-PAGE gels with prestained molecular standards. U, unbound DNA. The complexes observed are diagramed on the right.