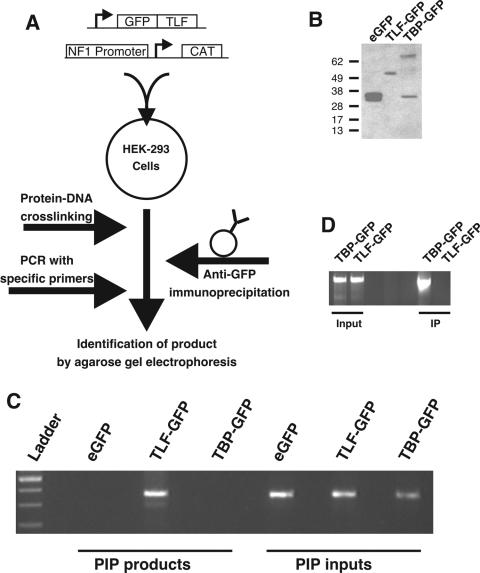
FIG. 3.
PIP showing that TLF binds directly to the pNF1-CAT reporter construct. (A) Diagrammatic representation of the PIP procedure. pNF1-CAT and GFP, TLF-GFP, or TBP-GFP were cotransfected into HEK-293 cells. After 40 h, treatment with 1% formaldehyde cross-linked the proteins to DNA. Subsequent immunoprecipitation with an anti-GFP antibody and proteinase K digestion allowed the identification of DNA regions that associate with fusion proteins. (B) The expression of GFP-containing TBP and TLF was verified by Western blot analysis with an anti-GFP antibody. (C) NF1 immunoprecipitates with TLF-GFP but not TBP-GFP or GFP. Cells transfected with the NF1 promoter plasmid and GFP, TLF-GFP, or TBP-GFP were subjected to PIP. A 350-bp band was detected by agarose gel electrophoresis (PIP products). The presence of the NF1 promoter plasmid in the cultures was verified by performing PCR with aliquots of the lysates removed just prior to mixing with agarose beads and purified by proteinase K digestion and phenol-chloroform extraction (PIP inputs). (D) The c-fos promoter associated with TBP-GFP but not TLF-GFP. Cells transfected with the c-fos promoter plasmid and TLF-GFP or TBP-GFP were subjected to PIP. A 2,100-bp band was detected by agarose gel electrophoresis (IP). The presence of the c-fos promoter plasmid in the cultures was verified by performing PCR with aliquots of the lysates (Input).