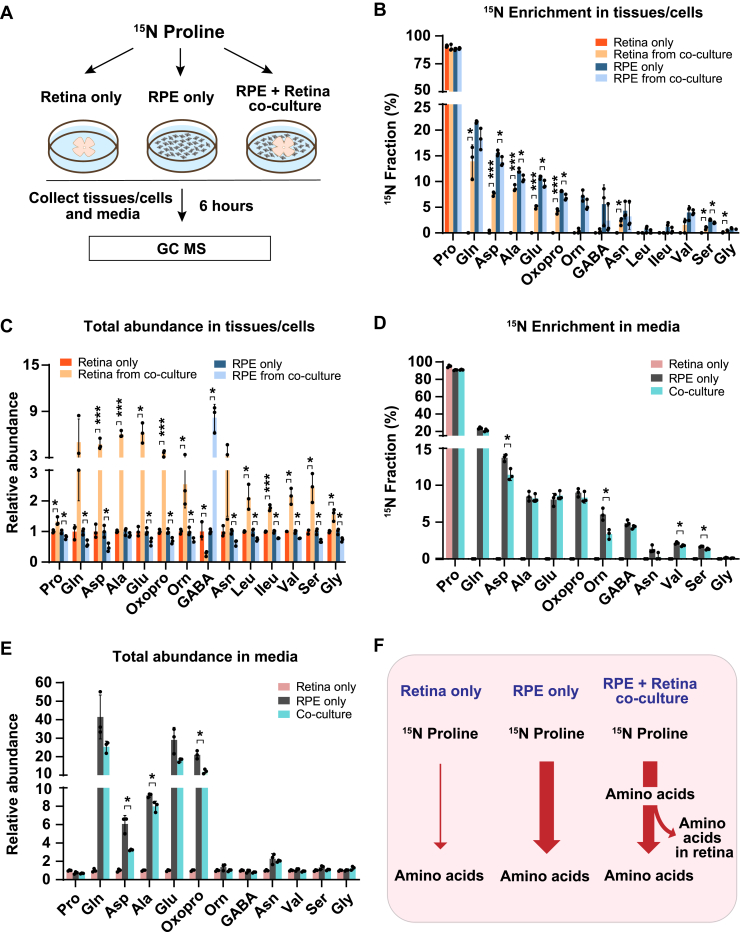
Figure 3.
The neural retina imports proline-derived amino acids from the RPE.A, human RPE cells and mouse retina were cultured separately or cocultured in DMEM with 1 mM 15N proline for 6 h. Tissues and media were collected for metabolite analysis with GC–MS. B and C, 15N fraction of metabolites derived from 15N proline in RPE cells/retina and the total abundance of all isotopologs in RPE cells/retina from coculture relative to their corresponding control. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, N = 3. D and E, 15N fraction of metabolites derived from 15N proline in media and the total abundance of all isotopologs in media relative to control media from the retina-only group. ∗p < 0.05, N = 3. F, a schematic of proline nitrogen metabolism in coculture. Retina alone barely utilizes proline for amino acid synthesis, but RPE utilizes proline to produce amino acids to feed the retina. Error bars represent SD. DMEM, Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.