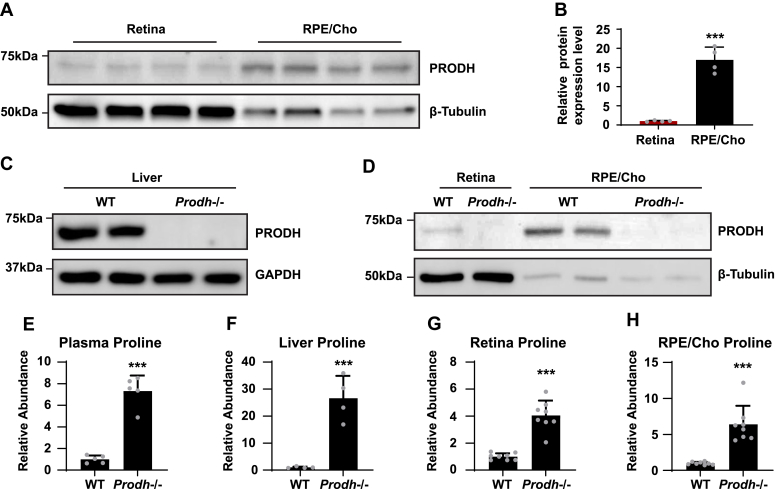
Figure 6.
PRODH is more abundant in the RPE/Cho, and deletion of Prodh causes proline accumulation.A, RPE/Cho has higher PRODH protein expression than RPE/Cho. β-tubulin is used as loading control. B, relative protein expression level of PRODH in retina and RPE/Cho. The relative protein level is the protein expression relative to the retina after normalized to the expression of tubulin. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, N = 4 (replicate lanes from four independent samples). C and D, Prodh mutation causes the depletion of PRODH proteins in liver, retina, and RPE/Cho in Prodh−/− mice. E–H, total abundance of proline in liver, plasma, RPE/Cho, and retina from Prodh−/− mice relative to those tissues from WT mice. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, N ≥ 4. Error bars represent SD. Cho, choroid; PRODH, proline dehydrogenase; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.