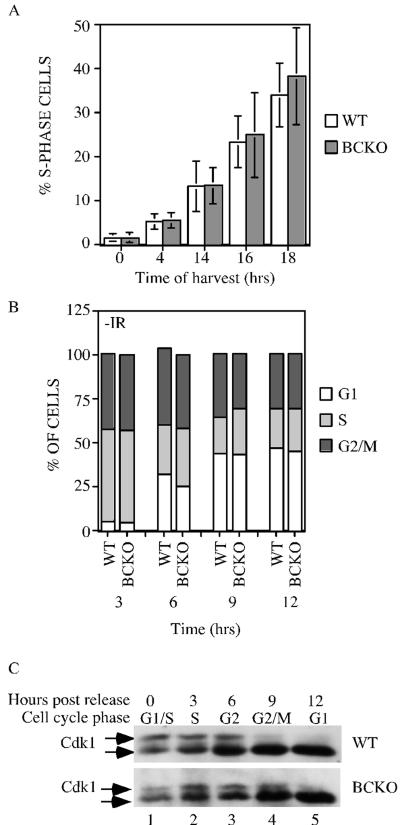
FIG. 2.
Cell cycle analysis of cells lacking Cdc25B and Cdc25C. (A) WT and BCKO MEFs (passages 4 to 6) were serum starved for 96 h to synchronize cells in G0. After the addition of serum, cells were incubated with BrdU for 1 h prior to harvest. Cells were stained with PI and for BrdU and were analyzed by flow cytometry. Each experiment was performed six times in duplicate with independent MEF strains, and standard deviations are shown as error bars along the y axis. Differences between WT and BCKO MEFs were not statistically different at any of the time points (0 h [P = 0.936], 4 h [P = 0.7374], 14 h [P = 0.9441], 16 h [P = 0.6278], and 18 h [P = 0.2667]). (B) MEFs at passages 4 to 6 were pulse labeled with BrdU for 1 h. Cells were harvested at the indicated times (hours) and stained with PI and for BrdU. The cellular DNA content of BrdU-positive cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Graphs show the averages from six independent experiments. (C) Early-passage MEFs prepared from wild-type and BCKO mice were synchronized in early S phase. Cells were harvested prior to release (time zero) or at various times (hours) after release. Cdk1 precipitates were resolved on a 12% SDS gel, and Cdk1 was detected by Western blotting. The arrows indicate two electrophoretic forms of Cdk1.