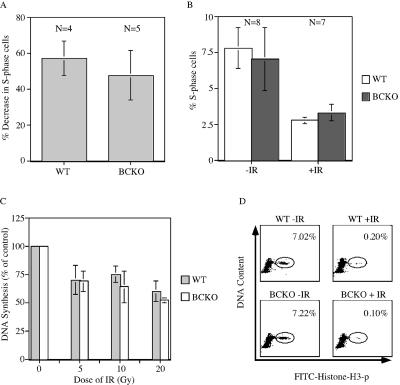
FIG. 3.
The IR-induced DNA damage checkpoint is intact in BCKO cells. (A) Early-passage MEFs were serum starved for 96 h. Arrested cells were mock irradiated or gamma irradiated and then incubated in BrdU-containing complete medium. Cells were stained with PI and for BrdU and analyzed by flow cytometry 24 h later. The percent decreases in S-phase cells following irradiation are indicated. Differences between WT and BCKO cells were not significant (P = 0.2909) (B) WT and BCKO mice were mock irradiated (−IR) or gamma irradiated (+IR) with 10 Gy of IR and injected intraperitoneally with BrdU 2 h later. One hour after the BrdU injection, thymocytes were prepared and analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentages of S-phase cells are indicated. Standard deviations are shown as error bars along the y axis. (C) Radioresistant DNA synthesis was assessed 1 h after the exposure of early-passage MEFs to various doses of IR. Experiments were repeated four times. Differences between WT and BCKO MEFs were not statistically different at any dose of IR (5 Gy [P = 0.9035], 10 Gy [P = 0.2095], and 20 Gy [P = 0.1333]). Standard deviations are shown as error bars along the y axis. (D) Early-passage MEFs were mock irradiated or gamma irradiated and incubated in nocodazole 40 min later. Cells were costained for DNA content and histone H3 phosphorylation (p) and were analyzed by flow cytometry 2 h after IR. The percentages of mitotic cells are indicated. The panels are representative results obtained using WT (n = 2) and BCKO (n = 3) MEFs.