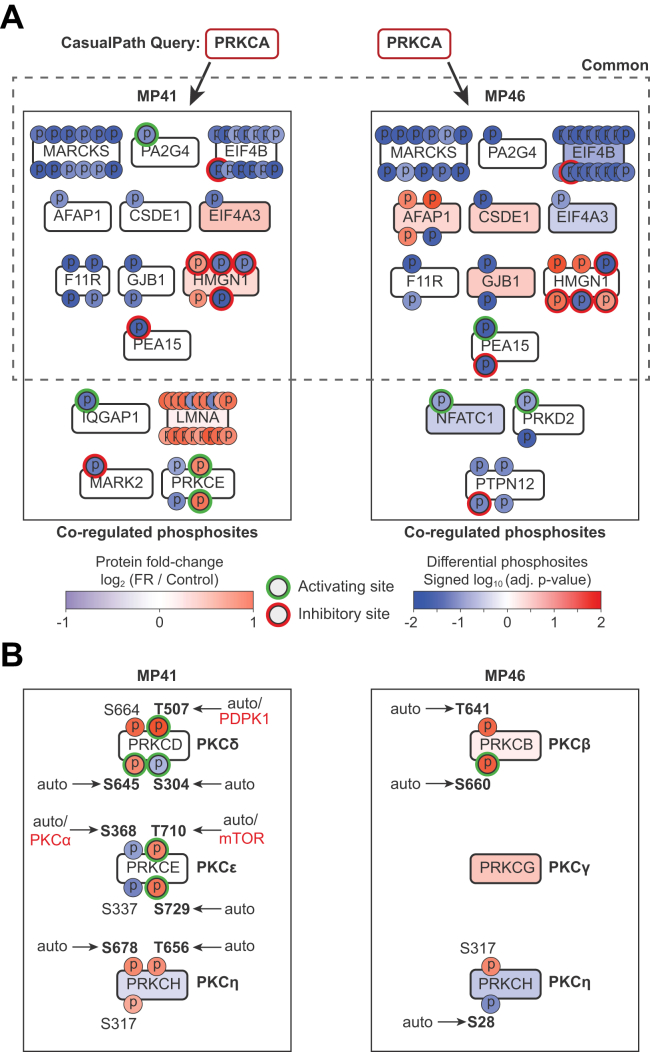
Fig. 3.
CausalPath analysis of PKC regulation by FR in UM cells.A, CausalPath generated subgraphs for PKCα (PRKCA) in both MP41 and MP46 UM cell lines, based on loss of phosphorylation of known targets in response to FR at FDR ≤ 0.001. Phosphorylation sites are red if increased with FR and blue if decreased. Color intensities for phosphorylation are based on adjusted p-values, as determined by CausalPath. Sites outlined in green are activation by phosphorylation, and those outlined in red are inhibited by phosphorylation. Protein levels are color coded based on log2 fold change with FR (red: increased; blue: decreased). Kinases outlined in red were inactivated by FR. Black boxes indicate coregulated targets of phosphorylation as defined by CausalPath for each cell line. Dashed box indicates targets of phosphorylation that are regulated in common between both cell lines. B, manual interrogation of other PKC isoforms identified by CausalPath in each cell line. Phosphosites in bold are known targets of autophosphorylation; other kinases that are known to target specific sites are indicated in red. Activities of these isoforms are determined by DAG and Ca2+ levels, such that these phosphosites are not specifically indicative of either activation or inactivation. FDR, false discovery rate; UM, uveal melanoma.