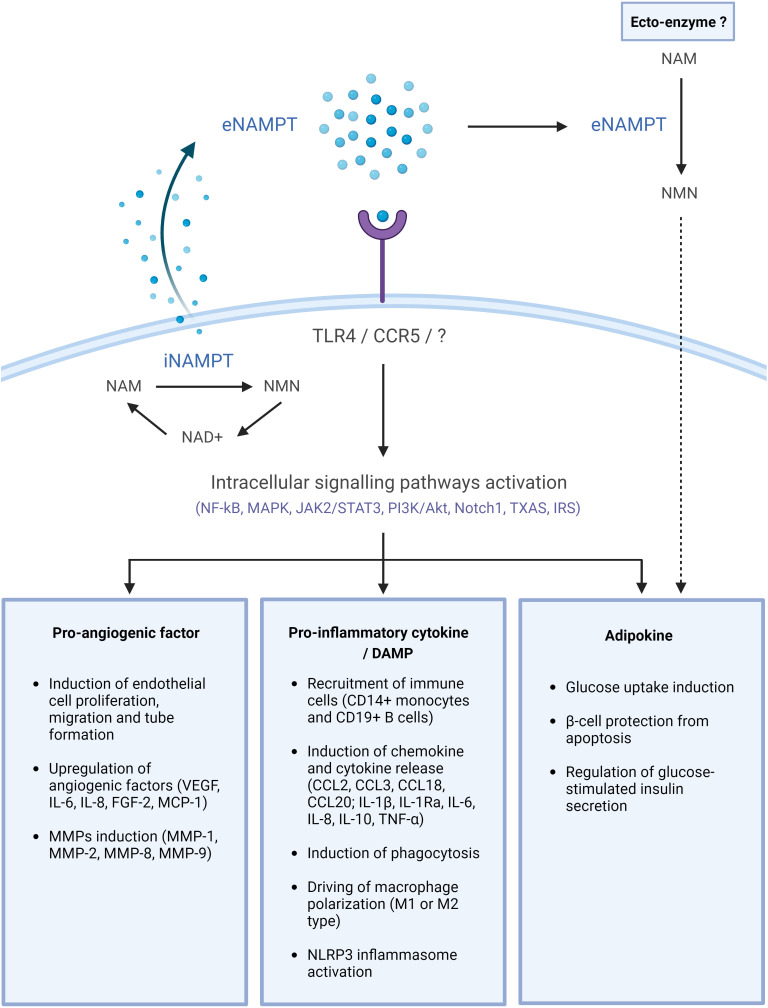
Figure 1.
eNAMPT, a DAMP/adipocytokine with multiple functions. NAMPT is released into the extracellular space through an unknown mechanism. There, it may bind cell surface receptors, including TLR4 or CCR5, and activate intracellular signaling pathways, eventually leading to the initiation of diverse physiological and/or pathological processes. eNAMPT may possibly also act as an ectoenzyme in the extracellular space, generating NMN, which can subsequently be internalized and participate in intracellular NAD biosynthesis. This image was created with BioRender.com. Akt, protein kinase B; CD, cluster of differentiation; CCL, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand; eNAMPT, extracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; IL, interleukin; IR, insulin receptor; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; JAK, Janus kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinases; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NAM, nicotinamide; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; Nocht1, neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TXAS, thromboxane synthase; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.