FIGURE 1.
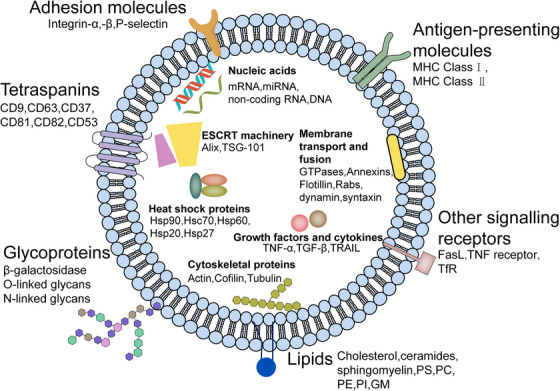
The composition of exosomes. Exosomes contain transmembrane proteins like tetraspanins (CD9, CD63, CD37, CD81, CD82, CD53), adhesion molecules (Integrin‐α,‐β, P‐selectin), antigen‐presenting molecules (MHC Class I, MHC Class II), glycoproteins (β‐galactosidase, O‐linked glycans, N‐linked glycans), and other signaling receptors (FasL, TNF receptor, TfR); as well as lumen proteins such as cytoskeletal proteins (actin, cofilin, tubulin), heat shock proteins (Hsp90, Hsc70, Hsp60, Hsp20, Hsp27), membrane transport and fusion proteins (GTPases, annexins, flotillin, Rab GTPases, dynamin, syntaxin), ESCRT machinery (alix, TSG‐101), and growth factors and cytokines (TNF‐α, TGF‐β, TRAIL); lipids (cholesterol, ceramides, sphingomyelin, PS, PC, PE, PI, GM); and nucleic acids (mRNA, miRNA, noncoding RNA, DNA). FasL, Fas ligand; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TfR, transferrin receptor; Hsp, heat shock protein; TSG, tumor susceptibility gene; TGF, transforming growth factor; TRAIL, TNF‐related apoptosis inducing ligand; PS, phosphatidylserine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PI, phosphatidylinositol; GM, gangliosides.
