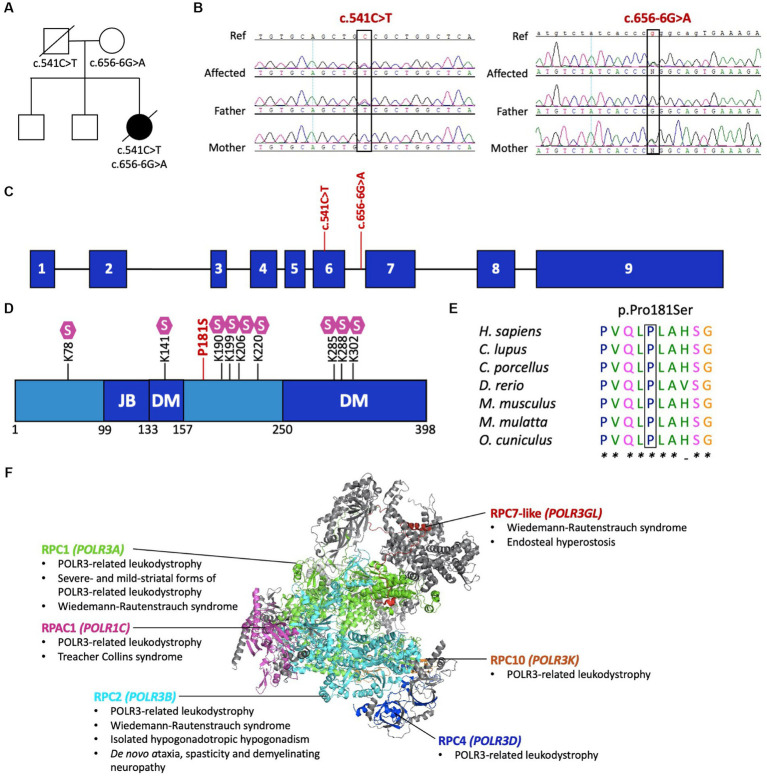
Figure 2.
Pathogenic variants in POLR3D. (A) Familial segregation of the c.541C > T (p.P181S) and c.656-6G>A (p.?). (B) POLR3D sequence chromatograms of the affected individual and her parents show segregation of the variants. (C) Schematic of POLR3D genomic DNA with pathogenic variants mapped. (D) Schematic of the domain organization of the RPC4 protein; JB, Jaw binding; DM, Dimerization domain. Lysine residues subjected to sumoylation (S) are marked on the sequence. The missense mutation (red) found in the patient described here is proximal to a sumoylation hotspot. (E) The missense variant in POLR3D is at a conserved amino acid residue. (F) Modeled human structure of RNA polymerase III. Colors identify Pol III subunits encoded by genes that harbor pathogenic variants, including POLR3A (green), POLR3B (cyan), POLR1C (magenta), POLR3D (blue), POLR3K (orange), and POLR3GL (red). Phenotypes associated with the genes are listed under the protein name. In all cases inheritance is autosomal recessive, except for de novo ataxia, spasticity, and demyelinating neuropathy. Modeled on PyMOL, PDB: 7A6H.