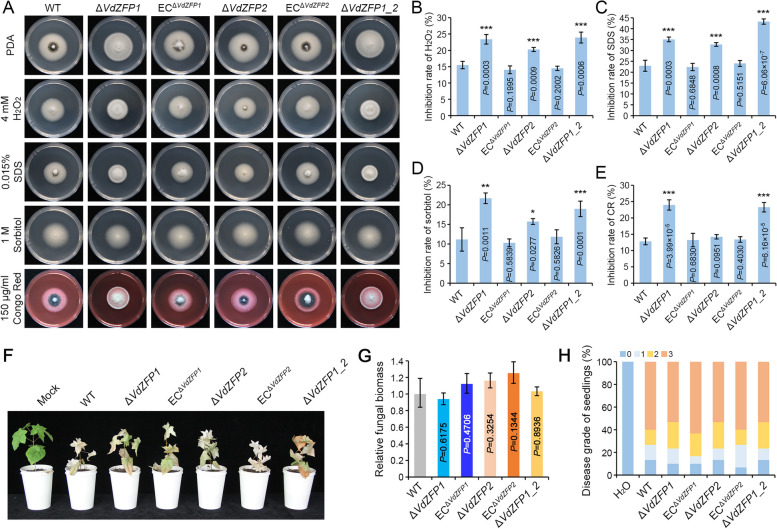
Fig. 8.
VdZFP1 and VdZFP2 contribute to the response of Verticillium dahliae to environmental stresses rather than pathogenicity. A Colony morphology of WT, ΔVdZFP1, ECΔVdZFP1, ΔVdZFP2, ECΔVdZFP1, and ΔVdZFP1_2 strains growth on medium supplemented with various stressors. These strains grown on PDA medium that supplemented with 4 mM H2O2, 0.015% SDS, 1 M sorbitol, and 150 μg/mL Congo red. The phenotypes were photographed 7 days after incubation at 25 °C in the dark. Each strain was inoculated at least 3 plates and repeated 3 times independently. B–E Sensitivity of indicated strains to stress factors. The inhibition rate of indicated strains responsible for various stressors in panel A. Error bars are standard errors calculated from six replicates, and this experiment performed three repeats. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (Student’s t test). Sensitivity of indicated strains to B H2O2, C SDS, D sorbitol, and E Congo red. F Pathogenicity assay of the indicated strains on shantung maple. Shantung maple seedlings were inoculated with WT, ΔVdZFP1, ECΔVdZFP1, ΔVdZFP2, ECΔVdZFP1, and ΔVdZFP1_2 strains, while the H2O treatment was set as negative control. The Verticillium wilt symptom were photographed at 50 dpi. G Quantification of the fungal biomass in maple stems by qPCR following inoculation of the indicated strains. Samples were collected from the stem base of infected plants at 50 dpi. The At18S gene of shantung maple was served as an endogenous control to evaluate the endophytic colonization of V. dahliae by quantifying VdEF-1α. The pathogenicity was analyzed with three replicates of 10 3-month-old maple trees, and the fungal biomass was calculated by three independent biological replicates. Error bars represent standard errors. P > 0.05 means not significant (one-way ANOVA). H Evaluation of disease grade of shantung maple seedlings. The disease grade was divided based on the Verticillium wilt symptoms and analyzed with three replicates of maple pathogenicity tests