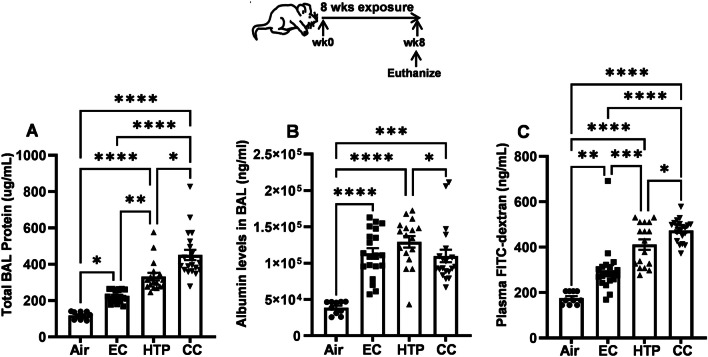
Fig. 5.
Chronic inhalatory exposure to aerosols from alternative tobacco products induces markers of lung damage. At the end of the 8-week exposures, mice were euthanized, BAL harvested and the levels of total proteins (A), albumin (B) in the BAL, and the levels of FITC-dextran (C) leaking into plasma were quantified as described previously [47] and given in detail in Additional file 1. Results are shown as bar diagrams with mean ± SE. Differences between groups is considered significant at p < 0.05 and are indicated as symbols *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001, calculated after performing non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test with FDR correction for multiple comparisons by employing GraphPad Prism V.9 software (GraphPad; La Jolla, California, USA). n = 10 animals for air (5M + 5F) and n = 20 animals for EC, HTP, and CC (10M + 10F)/group were used for each exposure condition