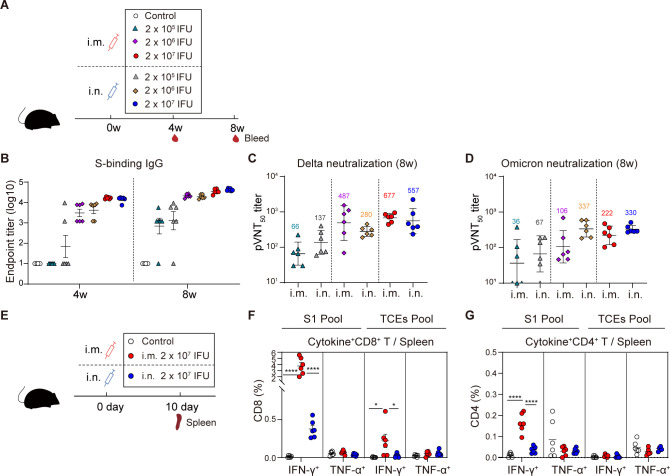
Fig 2.
Single-dose intramuscular immunization induced superior systemic T-cell responses over intranasal immunization. (A) Scheme of experiments. Mice (n = 6) were i.m. or i.n. immunized with 2 × 105, 2 × 106, and 2 × 107 IFU of AdC68-vST-vtRBM, respectively. About 100 µL PBS intramuscularly vaccinated mice served as control. Serum was collected at 4 and 8 weeks post-vaccination. (B) Serum anti-spike IgG titers. An ELISA was used to measure anti-spike lgG antibodies at 4 and 8 weeks post-vaccination. (C and D) The neutralizing activity against Delta (C) or Omicron (D) at 8 weeks post-vaccination. (E) Scheme of experiments. Mice (n = 6) were vaccinated with 2 × 107 IFU of AdC68-vST-vtRBM by i.m. or i.n. route, 100 µL PBS intramuscularly vaccinated mice served as control. Mice were euthanized at 10 days post-vaccination. Spleens were harvested for effector T-cell detection. (F and G) Frequencies of splenic CD8+ T cells (F) and CD4+ (G) T cells producing IFN-γ, TNF-α following re-stimulation with peptide pools for S1 and TCEs. Values of geometric mean titer (GMT) were displayed in (C) and (D). Data are represented as GMT ± SD (C and D) or mean ± SEM (B, F and G). One-way ANOVA with Tukey correction was used for multiple comparisons. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001.