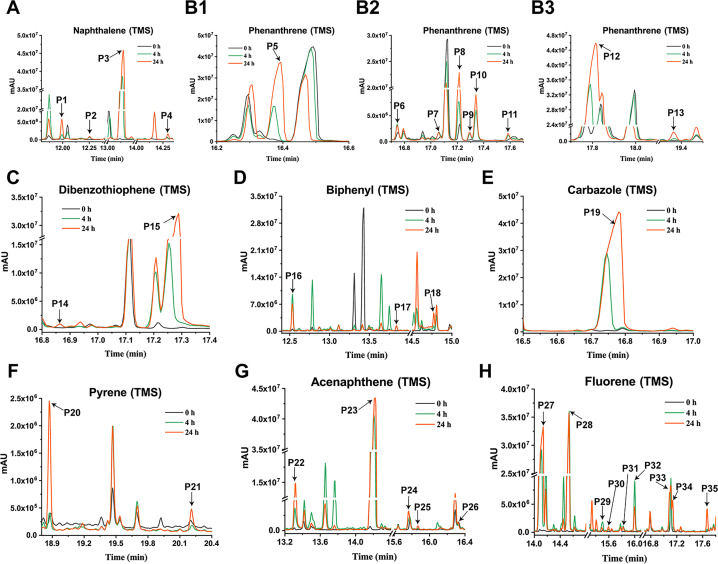
Fig 3.
GC-MS profile of degradation samples of PAHs and their derivatives by E. coli BL21(DE3) with heterologous expression of NarA2B2 and PhtAcAd. The sample at 0 h was used as the control, and the samples at 4 and 24 h were the experimental group. (A) Naphthalene (P1: 1-naphthol, TMS; P2: 2-naphthol, TMS; P3: NAP-1,2-dihydrodiol, 2TMS; P4: 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene, 2TMS). (B1–B3) Phenanthrene (P6, P7, P9, P10, P11: monohydroxy-PHE, TMS; P5: PHE-9,10-dihydrodiol, 2TMS; P8, P12: PHE-dihydrodiol, 2TMS; P13: dihydroxyl-PHE, 2TMS). (C) Dibenzothiophene (P14: monohydroxy-DBT, TMS; P15: dibenzothiophene-S-oxide). (D) Biphenyl (P16: 4-phenylphenol, TMS; P17: 3-hydroxybiphenyl, TMS; P18: 2,2-biphenyldiol, 2TMS). (E) Carbazole (P19: monodroxy-CA, TMS). (F) Pyrene (P20: PYE-4,5-dihydrodiol, 2TMS; P21: monodroxy-PYE, TMS). (G) Acenaphthene (P22: 1-acenaphthenone; P23: 1-acenaphthenol, TMS; P24–25: 1,2-dihydroxyacenaphthene, 2TMS; P26: 1,2-dihydroxyacenaphthylene, 2TMS). (H) Fluorene (P27: 9-fluorenone; P28: 9-fluorenol, TMS; P29-31: monodroxy-FLN, TMS; P32: 2-fluorenol, TMS; P33, P35: dihydroxy-FLN, 2TMS; P34: 2-hydroxy-9-fluorenone, TMS).