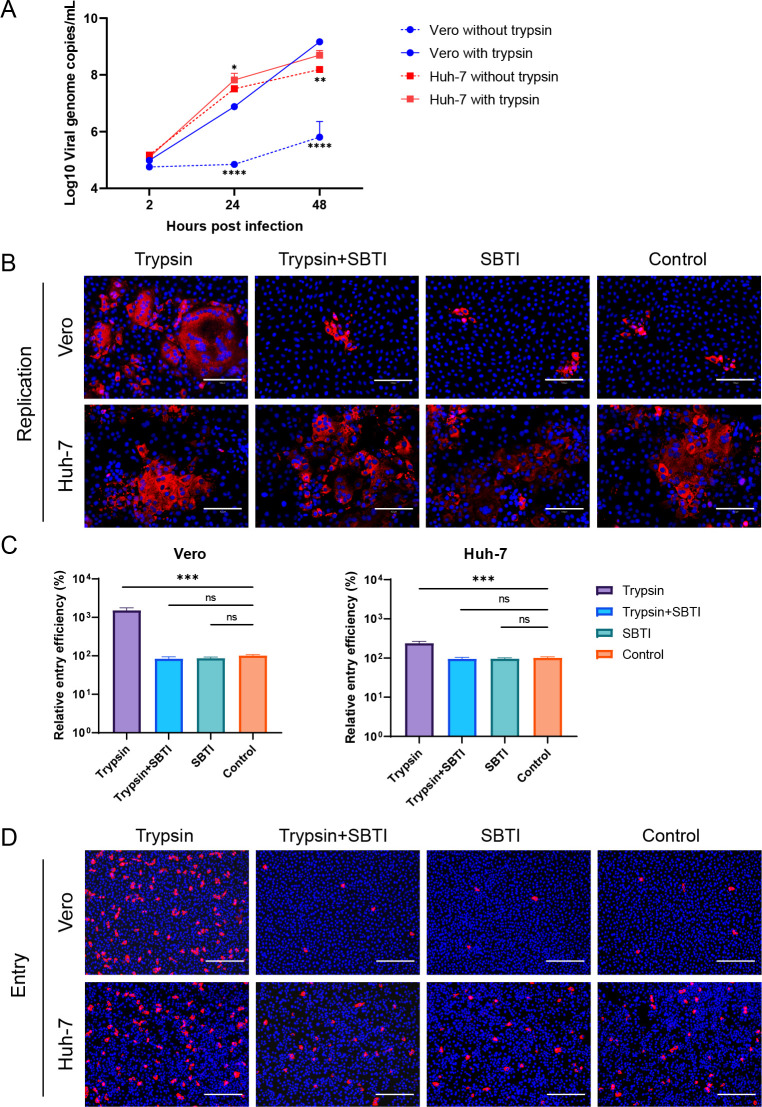
Fig 4.
Effects of trypsin on SADS-CoV infection. (A) For the detection of viral replication dynamics, Vero and Huh-7 cells were infected with SADS-CoV (MOI = 0.1) and treated with or without 4 µg/mL trypsin. The supernatants were harvested at 0, 24, or 48 hpi for the assessment of viral replication dynamics by qRT-PCR. (B) Vero and Huh-7 cells were infected with SADS-CoV (MOI = 0.1) and treated with 4 µg/mL and/or 10 µg/mL TBSI. The cells were fixed at 24 hpi and stained with anti-SADS-CoV NP antibodies by IFA. For viral entry detection, Vero and Huh-7 cells were infected with SADS-CoV (MOI = 1) in the presence of 4 µg/mL trypsin and/or 10 µg/mL TBSI for 6 h. The cells were then lysed, and virus detection was performed using qRT-PCR (C). Alternatively, cells were fixed and stained with anti-SADS-CoV NP antibodies by IFA (D). All data are shown as means ± standard errors of the means (n = 3 biological replicates). Scale bars: 125 µm (B) and 300 µm (D).