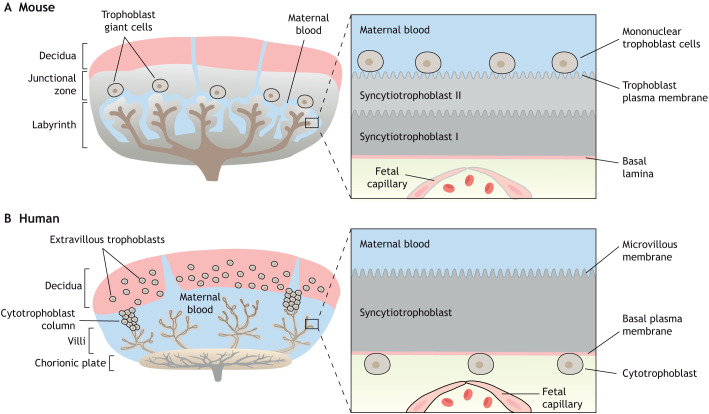
Fig. 2.
Comparison of mouse and human placental structures. (A,B) Both mouse and human placentas are hemochorial (trophoblast bathed in maternal blood) and discoid in shape. (A) The murine placental structure includes the labyrinth and junctional zones. The box depicts the maternal-fetal interface of the labyrinth, demonstrating the haemotrichorial or three trophoblast layers (a mononuclear trophoblast cell layer and syncytiotrophoblast layers I and II). (B) The human placenta has analogous layers: a decidual layer with spiral arteries and the placental villi. The box details a section of a chorionic villus illustrating the haemomonochorial or monolayer of syncytiotrophoblast cells separating maternal and fetal blood. The apical brush border of the human syncytiotrophoblast in contact with maternal blood is referred to as microvillous membrane (MVM) and the opposing plasma membrane juxtaposed to the fetal capillary is referred to as basal membrane (BM). The corresponding apical membrane in the mouse placenta is referred to as the trophoblast plasma membrane (TPM) and is localized to syncytial layer II.