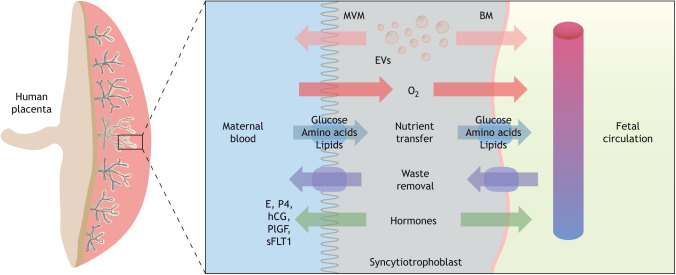
Fig. 3.
Human placental morphology and transport across the maternal-fetal interface. Transport across the syncytiotrophoblast occurs via passive and facilitated diffusion, active transport and endo- and exocytosis. Macromolecules and waste products are transported across the syncytiotrophoblast via specialized transporting proteins, channels and exchangers located in the plasma membranes. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) and hormones released by the syncytiotrophoblast cells are released to the maternal and fetal circulations, thereby participating in maternal-fetal cross-talk. BM, basal plasma membrane; E, estrogen; P4, progesterone; hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin; MVM, microvillous membrane; plGF, placental growth factor; sFLT1, soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase.