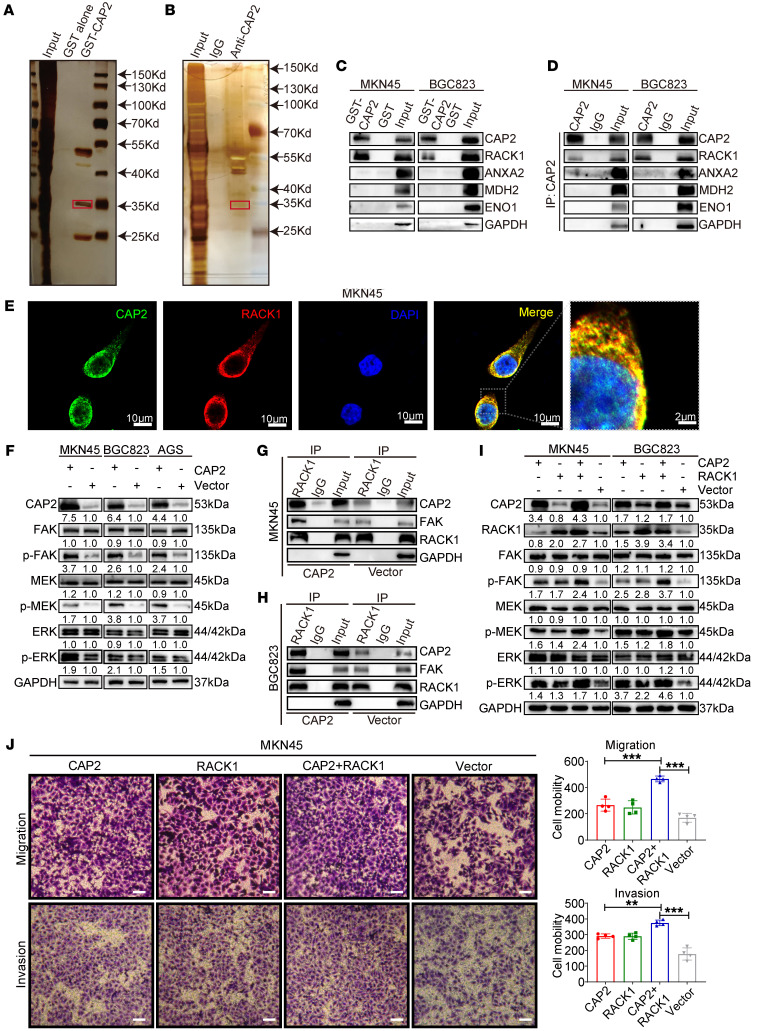
Figure 4. CAP2 binds to RACK1 and activates the FAK/MEK/ERK axis.
(A) Pull-down experiments were performed on lysates from MKN45 cells using GST-CAP2 or GST-tagged proteins, followed by gel electrophoresis. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was performed on 30- to 70-kDa proteins. (B) Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-CAP2 or IgG. The co-IP elutions were silver-stained, and all coimmunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. (C) In vitro binding between RACK1 and GST-CAP2 was analyzed by GST pull-down assays. (D) Co-IP showed that RACK1 was immunoprecipitated by CAP2, rather than ANXA2, MDH2, or GAPDH. (E) Immunofluorescence analysis showed the CAP2/RACK1 colocalization in MKN45 cells. Scale bars: 10 μm; 2 μm (right). (F) Effects of CAP2 on FAK/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in GC cells were detected by Western blot. (G and H) Effects of CAP2 on the binding strength of RACK1/FAK complex were detected by co-IP assays. (I) Effects of CAP2 and RACK1 on FAK/MEK/ERK signaling pathway were detected by Western blot. (J) The migration ability of GC cell lines was determined by Transwell assay. Scale bars: 50 μm (n = 4). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (J).