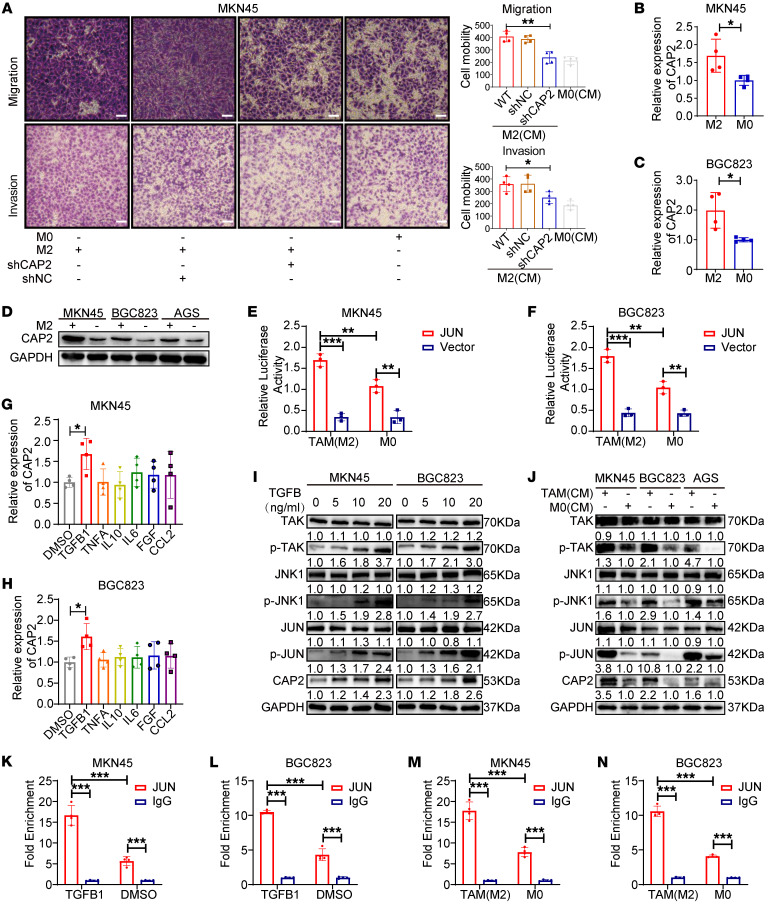
Figure 7. TAMs promote CAP2 expression through TGFB1-mediated activation of JUN.
(A) The migration and invasion abilities of GC cells were determined by Transwell assay after the GC cells were induced by TAM-conditioned medium (n = 4). Scale bars: 50 μm. (B and C) Expression of CAP2 in GC cells induced by TAM-conditioned medium was detected by RT-PCR (n = 4). (D) Expression of CAP2 in GC cells induced by TAM-conditioned medium was detected by Western blotting. (E and F) Luciferase activity was detected after the GC cells were induced by TAM-conditioned medium (n = 3). (G and H) Expression of CAP2 was detected by RT-PCR after the GC cells were treated with cytokines (n = 4). (I) Expression of TAK/JNK/JUN signaling pathway proteins was detected by Western blotting after the GC cells were treated with TGFB1. (J) Expression of TAK/JNK/JUN signaling pathway proteins was detected by Western blotting after the GC cells were induced by TAM-conditioned medium. (K and L) The binding ability of JUN to the CAP2 promoter region was detected by ChIP after the GC cells were treated with TGFB1 (n = 4). (M and N) The binding ability of JUN to the CAP2 promoter region was detected by ChIP after the GC cells were induced by TAM-conditioned medium (n = 4). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (A, G, and H), 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (B and C), 2-way ANOVA test (E, F, and K–N). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.