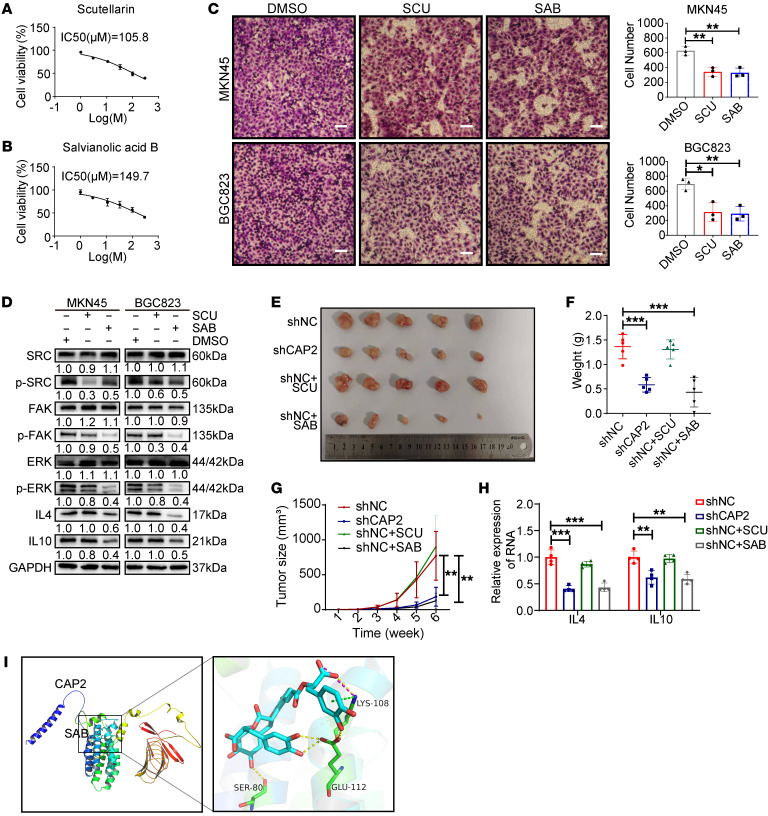
Figure 8. Salvianolic acid B is a putative molecular inhibitor of CAP2 and suppresses GC progression.
(A and B) IC50 determination of scutellarin (SCU) and salvianolic acid B (SAB) on MKN45 cells. After treatment of GC cells with a series of doses (1, 3.5, 11, 33, 100, and 300 μM) of inhibitors for 48 hours, cell viability was determined by CCK-8 assay. (C) Transwell migration assay of GC cells treated with SCU and SAB. Scale bars: 50 μm. (D) Protein expression of SRC/FAK/ERK/IL-4/IL-10 was determined by Western blotting after the GC cells were treated with SCU and SAB. (E and F) Mice subcutaneously injected with LV-NC MKN45 cells were treated with SCU and SAB, and then xenograft tumors were extracted (E) and weighed (F). (G) The growth curves of xenograft tumors were plotted based on the tumor size. The tumor size (V) was calculated based on the equation V = (length × width2)/2 (n = 5). (H) RNA expression of IL4 and IL10 in tumors was determined by quantitative PCR (n = 4). (I) Autodock predicts molecular docking of CAP2 with salvianolic acid B. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (C, F, and H), 2-way ANOVA test (G).