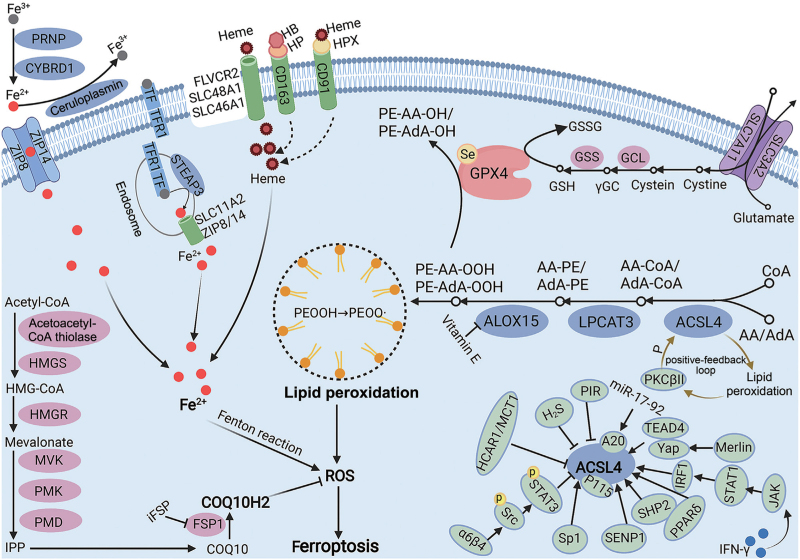
Figure 1.
ACSL4 is indispensable for triggering ferroptosis by generating lipid peroxidation. ACSL4 could first catalyze the insertion of CoA into AA and AdA, followed by the esterification of AA-CoA and AdA-CoA into PEs with the assistance of LPCAT3. Then, ALOX15 oxidizes AA-PE and AdA-PE into PE-AA-OOH and PE-AdA-OOH, triggering ferroptosis at cellular membranes. The GPX4/GSH system could reduce PE-AA/AdA-OOH to PE-AA/AdA-OH and, thus, ameliorate lipid peroxidation-mediated ferroptosis. In addition, the Fenton reaction by Fe2+ could generate ROS, while COQ10H2 produced by the MVA pathway could alleviate ROS. Regulators of ACSL4, such as TEAD4, YAP, IRF1, PPARδ, SHP2, SENP, p115, Sp1, α6β4, HCAR1/MCT1, PIR, and A20, are also summarized in the figure. Created with BioRender.com. AA: Arachidonic acid; AA-CoA: Arachidonoyl-coenzyme A (CoA); ACSL4: Acyl-CoA synthase 4; AdA: Adrenic acid; ALOX15: ACSL4/LPCAT3/acid-15-lipoxygenase; CD163: Cluster of differentiation 163; CD91: Cluster of differentiation 91; COQ10: Coenzyme Q10; COQ10H2: Reduced COQ10; CYBRD1: Cytochrome B reductase 1; FLVCR2: Feline leukemia virus subgroup C receptor-related protein 2; FSP1: Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; GCL: Glutamate cysteine ligase; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH: Glutathione; GSS: Glutathione synthase; GSSG: Oxidized glutathione; HB: Hemoglobin; HCAR1: Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1; HMG-CoA: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A; HMGR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A reductase; HMGS: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A synthase; HP: Haptoglobin; HPX: Hemopexin; H2S: Hydrogen sulfide; IPP: Isopentenyl diphosphate; IRF1: Interferon regulatory factor 1; IFN-γ: Interferon γ; JAK: Janus kinase; LPCAT3: Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; MCT1: Monocarboxylate transporter 1; miR: MicroRNA; MVA: Mevalonate; MVK: Mevalonate kinase; P: Phosphorylation; PE: Phosphatidylethanolamine; PIR: Pirin; PMD: Phosphomevalonate decarboxylase; PMK: Phoshpomevalonate kinase; PKCβII: Protein kinase C-beta II; PRNP: Prion protein; PPARδ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SENP: Sentrin-specific protease; SHP2: Src homology-2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2; SLC3A2: Solute carrier family 3 member 2; SLC7A11: Solute carrier family 7 member 11; SLC11A2: Solute carrier family 11 member 2; SLC46A1: Solute carrier family 46 member 1; SLC48A1: Solute carrier family 48 member 1; Sp1: Specificity protein 1; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; STEAP3: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 3; TEAD4: Transcriptional enhanced associate domain 4; TF: Transferrin; TFR1: Transferrin receptor 1; Yap: Yes-associated protein; ZIP: Zinc-and iron-related protein; γ-GC: γ-glutamylcysteine.