FIGURE 1. Phase 1 Assessment Flowchart for Credibility of Sources of Health Information in Social Media.
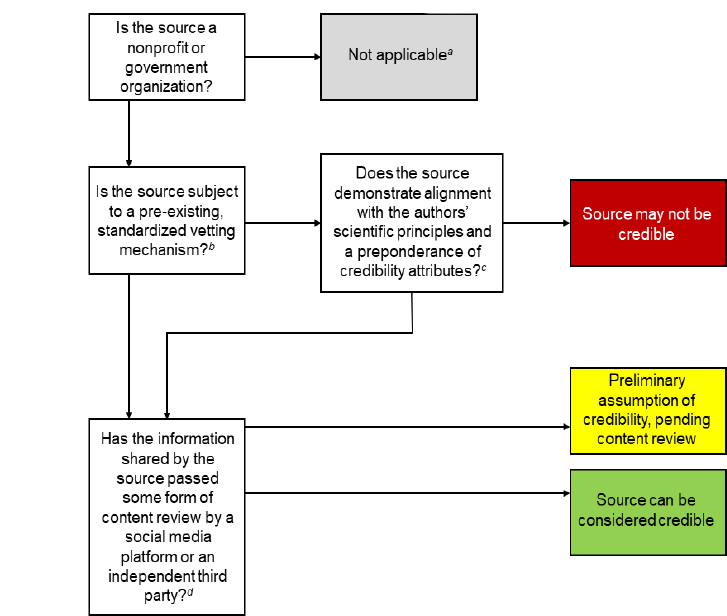
SOURCE: Kington, R., S. Arnesen, W-Y. S. Chou, S. Curry, D. Lazer, and A. Villarruel. 2021. Identifying Credible Sources of Health Information in Social Media: Principles and Attributes. NAM Perspectives. Discussion Paper, National Academy of Medicine, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.31478/202107a.
NOTES: [a] This chart is developed for credibility assessment of nonprofit and government organizations only. For-profit companies and individuals that serve as sources of health information should also undergo separate credibility assessment processes.
[b] Pre-existing, standardized vetting mechanisms that align with the authors' principles and attributes include accreditation, academic journal indexing, and government accountability rules. Even sources subject to one of these mechanisms should strive to meet the authors' stated credibility principles and attributes.
[c] See Table 1 for a list of principles and credibility attributes.
[d] Ideally, a quality assurance system that includes content assessment should supplement assessment of source credibility.
