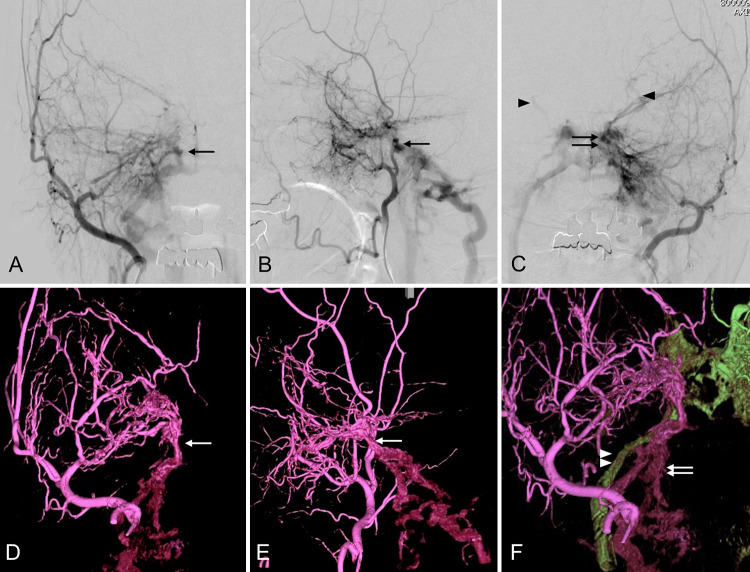
FIG. 1.
Angiography of the right external carotid artery (ECA) in the anteroposterior (A) and lateral (B) projections shows that the right-sided shunt point is slightly lower than the left (arrow). Left ECA angiography (C) shows a cavernous sinus (CS) dural arteriovenous shunt (double arrows) and shunt flow reflux to the bilateral superior ophthalmic veins (arrowheads). Three-dimensional rotational angiography (3D-RA) of the right ECA in the anteroposterior (D) and lateral (E) projections reveals that multiple feeders cluster the shunt point (white arrow) and that the shunt flow does not drain into the CS but into the caudal. The 3D fusion image (F) of the bilateral ECA shows that the right and left arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) had different drainage routes. The shunt flows from the left ECA draining into the internal jugular vein (IJV) via the left inferior petrosal sinus (IPS; green drainage route, white arrowheads). In contrast, the shunt flows from the right ECA drain into a different route (purple drainage route, white arrows).