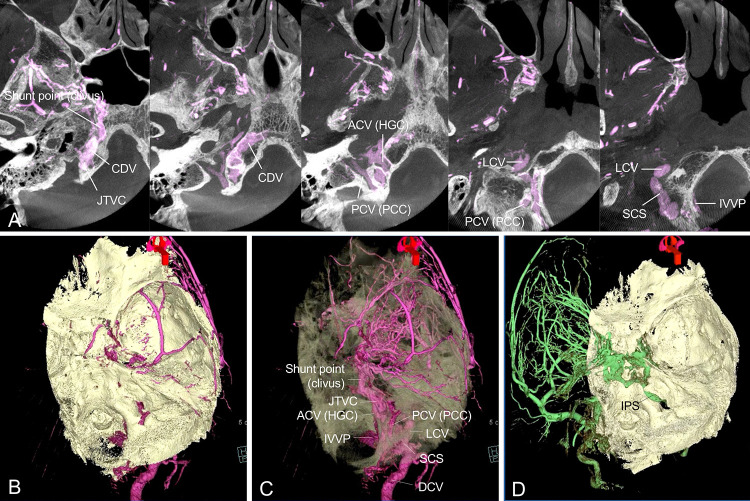
FIG. 2.
The fusion image of cone-beam computed tomography (CT) and 3D-RA of the right ECA. The axial slice image (A) shows the shunt point in the right clivus. The shunt flow drains into extracranial veins such as the lateral condylar vein (LCV), suboccipital cavernous sinus (SCS), internal vertebral venous plexus (IVVP), and deep cervical vein (DCV) through the jugular tuberculum venous complex (JTVC) from the anterior condylar vein (ACV) within the hypoglossal canal (HGC) and the posterior condylar vein (PCV) within the posterior condylar canal (PCC). Volume-rendering fusion image of the right ECA angiography (B and C). Intracranial shunt flow is not observed because the AVF exists within the skull (B). The skull translucency image (C) reveals intraosseous venous flow within the clivus and jugular tuberculum. Volume-rendering fusion image (D) of the left ECA angiography shows the left CS dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF). CDV = clival diploic vein.