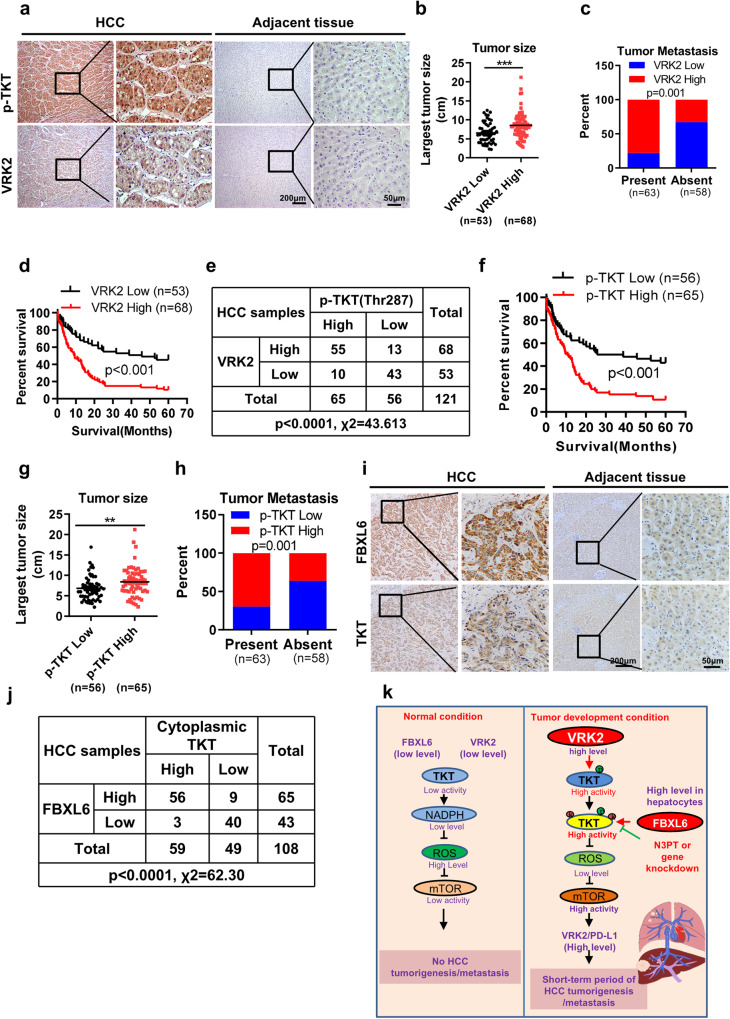
Fig. 7. The activated TKT protein level correlates positively with the protein levels of FBXL6 and VRK2 and predicts unfavorable survival in HCC patients.
a Tissue sections of adjacent normal or HCC tissue from patients were subjected to IHC staining for p-Thr287 TKT and VRK2. Representative images are shown. Scale bar, 200 μm or 50 μm. b, c High expression of VRK2 was positively associated with tumor size and metastasis. d The prognostic significance of VRK2 in HCC patients was evaluated by Kaplan–Meier analysis. High expression of VRK2 predicted a shorter overall survival time. e The association between the p-Thr287 TKT and VRK2 protein levels was evaluated by the χ2 test in 121 HCC tissues. f The prognostic significance of p-Thr287 TKT in HCC patients was evaluated by Kaplan–Meier analysis. g, h A high level of p-Thr287 TKT was positively associated with tumor size and metastasis. i Tissue sections of adjacent normal or HCC tissue from patients were subjected to IHC staining for cytoplasmic TKT and FBXL6. Representative images are shown. Scale bars, 200 μm or 50 μm. j The association between cytoplasmic TKT and FBXL6 was evaluated by the χ2 test in 108 HCC tissues. **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001. k A model of FBXL6-driven HCC tumorigenesis and metastasis in vivo. Under physiological conditions, hepatocytes with low levels of FBXL6 and VRK2 expression have lower levels of TKT phosphorylation and ubiquitination; thus, TKT activity is maintained at a low level. Upon FBXL6 upregulation in hepatocytes, TKT is first phosphorylated at Thr287 by VRK2. The phosphorylated TKT is then recognized and ubiquitinated at K16/319 by SCF-FBXL6, which promotes TKT activation and cytoplasmic localization. Activated TKT can upregulate VRK2 and PD-L1 expression through a decrease in ROS accumulation and activation of mTOR, leading to immune escape and HCC metastasis.