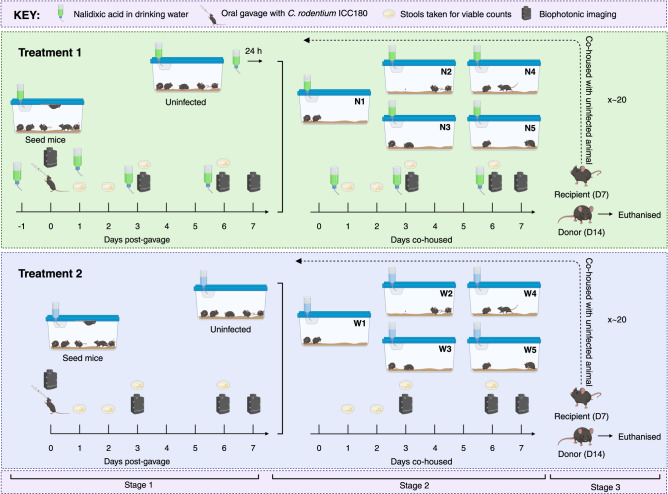
Fig. 1. Experimental schematic summarising the establishment of ten mouse-to-mouse Citrobacter rodentium ICC180 transmission chains.
Seed mice were split into two treatment groups (with nalidixic acid added to the drinking water every 2–3 days [N] or without [W]) and orally gavaged with ICC180. Seven days post-gavage, donor animals were transferred to individual cages (N1-5/W1-5) and cohoused with an uninfected cage-mate (recipient). After 7 days, the donor was humanely euthanized. The recipient then became the donor for the next step in the transmission chain by being transferred to a clean cage and cohoused with an uninfected cage-mate. This cycle was repeated until the end of the experiment. Infection and transmission dynamics were monitored by measuring luminescence and viable bacterial counts from stool samples and in vivo by biophotonic imaging.